
Social
Security (Jersey) Law 1974[1]
A LAW to establish a scheme of social
security and for connected purposes
Commencement
[see endnotes]
PART 1
INTRODUCTORY
1 Interpretation
(1) In
this Law, unless the context otherwise requires –
“1961 Law” means the Income Tax (Jersey)
Law 1961;
“appointed day” has the
meaning assigned thereto by Article 54;
“benefit” means benefit
under this Law;
“claimant”, in Articles 34A,
34B and 34D –
(a) means a person claiming
long term incapacity allowance; and
(b) also means, in relation
to the review of a decision, any beneficiary affected by the decision;
“contract of service”
means any contract of service or apprenticeship, whether written or oral, and
whether expressed or implied;
“earnings” –
(a) in
relation to a Class 1 insured person, has the meaning given in Schedule 1A;
(b) in
relation to a Class 2 insured person, has the meaning given in Schedule 1B;
“employed person” and “employed
person’s employment” have the meanings assigned thereto by Article 3;
“Health Insurance Fund”
means the Fund established and so called by virtue of Article 21 of the Health Insurance
(Jersey) Law 1967;
“Health Insurance Fund
allocation” has the meaning assigned thereto by Article 30;
“incapable of work” means
incapable of work by reason of some specific disease or bodily or mental
disablement or deemed, in accordance with the provisions of any Order, to be so
incapable;
“insured person” means,
for all the purposes of this Law, a person described in Article 3(1) and
includes, for the purposes only of the liability to pay LTC contributions, a
person described in Article 3(1A);
“Jersey
Index of Earnings” means the Index of Average Earnings produced by Statistics Jersey (within the meaning assigned by Article 2 of
the Statistics and
Census (Jersey) Law 2018);
“Law of 1950” means
the Insular Insurance (Jersey) Law 1950;
“Long-Term Care Fund”
means the Fund established under Article 2 of the Long-Term Care (Jersey)
Law 2012;
“Long-Term Care Fund
allocation” has the meaning given by Article 30;
“LTC contributions” means
long-term care contributions;
“medical board” means a
board appointed under Article 34AA;
“medical examination”
includes bacteriological and radiographical tests and similar investigations,
and references to being medically examined shall be construed accordingly;
“medical practitioner”
means –
(a) a “registered medical
practitioner” as defined in Article 1(1) of the Medical Practitioners
(Registration) (Jersey) Law 1960; or
(b) a “fully registered
person” as defined in section 55 of the Medical Act 1983 of the
United Kingdom;
“Minister” means the Minister for
Social Security;
“Order” means an Order
made by the Minister under this Law;
“pensionable age” shall be
construed in accordance with Article 1A;
“prescribed” means
prescribed by Order;
“relevant contribution
conditions” means, in relation to benefit of any description, the contribution
conditions for benefit of that description as set out in Schedule 2;
“relevant
disease or injury” means, in relation to
long term incapacity allowance, the disease or injury in respect of which that
benefit is claimed or payable;
“relevant loss of faculty”
means the loss of faculty resulting from the relevant disease or injury;
“Social Security Fund” has
the meaning assigned thereto by Article 30;
“Social Security Medical
Appeals Tribunal” means the Tribunal constituted under Article 34;
“Social Security Tribunal”
means the Tribunal constituted by
Order under Article 33A;
“standard
contribution” –
(a) in
relation to a Class 1 insured person, has the meaning given in Schedule 1A;
(b) in
relation to a Class 2 insured person, has the meaning given in Schedule 1B;
“standard rate of
benefit” –
(a) for the purposes of the
old age pension, has the meaning given in Part 1A of Schedule 1;
(b) for the purposes of any
other benefit, has the meaning given in Article 13(2).[2]
(2) For
the purposes of this Law –
(a) “child” means a child
below school leaving age and any other child who is in full-time education;
(b) a person shall be treated
as having a family that includes a child if he or she lives with any child as
part of his or her household;
(c) “school leaving age”
means the upper limit of compulsory school age by virtue of Article 2 of
the Education
(Jersey) Law 1999. [3]
(3) For
the purposes of this Law –
(a) a person shall be deemed
to be over or under any age therein mentioned if the person has or has not
attained that age;
(b) a person shall be deemed
to be between 2 ages therein mentioned if the person has attained the
first-mentioned age but has not attained the second-mentioned age.
(4) For
the purposes of this Law, 2 persons shall not be deemed to have ceased to
reside together by reason of any temporary absence of either or both of them,
and in particular by reason of any such absence at school or while receiving
medical treatment as an in-patient in a hospital or similar institution or by
reason of any absence of either or both of them in such circumstances as may be
prescribed.
(5) The
Minister may by Order prescribe, for any specified purpose or provision of this
Law –
(a) monetary amounts and
benefits of any description (whether or not convertible into money) that are,
or are not, earnings;
(b) without prejudice to the
generality of sub-paragraph (a), descriptions of income that are to be
treated as earnings;
(c) the manner in which the
value attributable to any earnings that are not money is to be determined;
(d) when any earnings are
deemed to be paid;
(e) circumstances in which
notional earnings are to be attributed to a person;
(f) the manner in which a
person’s earnings are to be calculated or estimated;
(g) the manner in which the
amount of a person’s earnings to be treated as comprised in any payment made to
or in respect of the person is to be calculated or estimated; and
(h) earnings of a specified
class or description, made or falling to be made to or by a person, that are to
be disregarded, wholly or in part, in calculating a person’s earnings, or
deducted from such earnings.[4]
(6) [5]
(7) [6]
(8) For
the purposes of this Law, a police officer in the States of Jersey Police Force
is to be taken to be an employee of the Chief Officer of that Force under a
contract of service.[7]
1A Pensionable age[8]
Schedule 1AA has
effect to specify what, in any person’s case, is the person’s pensionable age.
2 General administration[9]
PART 2
INSURED PERSONS AND CONTRIBUTIONS
3 Description and
classification of insured persons
(1) Subject
to the provisions of this Law, every person who immediately before the
appointed day was an insured person under the Law of 1950, and every person
who has attained school leaving age on, or who attains school leaving age
after, the appointed day and who fulfils such conditions as to residence in
Jersey as may be prescribed, shall become insured under this Law and thereafter
continue throughout his or her life to be so insured.
(1A) Subject
to the provisions of this Law, a person who attains school leaving age and is
deemed, in prescribed circumstances, to be resident in Jersey, shall be insured
under this Law for the purposes only of the liability to pay LTC contributions.[10]
(2) For
the purposes of this Law, insured persons shall be divided into the following 2
classes –
(a) Class 1, which shall
comprise employed persons, that is to say, persons gainfully occupied in
employment in Jersey under a contract of service; and
(b) Class 2, which shall
comprise persons not in Class 1.
Hereafter in this Law any
employment by virtue whereof an insured person is an employed person is
referred to as an “employed person’s employment”.
(3) Provision
may be made by Order for modifying the said classification in relation to cases
where it appears to the Minister desirable by reason of the nature or
circumstances of a person’s employment or otherwise.
4 Source of funds
(1) For
the purpose of providing the funds required for paying benefit and for making
any other payments which under this Law are to be made out of the Social
Security Fund, and for providing the Health Insurance Fund allocation and the
Long-Term Care allocation each specified in Article 30, contributions
shall be payable by insured persons and employers in accordance with the
provisions of this Law.[11]
(2) Contributions
shall be of the following 3 classes –
(a) Class 1 contributions
payable in respect of Class 1 insured persons being made up of –
(i) employed persons’ primary Class 1
contributions, and
(ii) employers’ secondary
Class 1 contributions;
(b) Class 2 full rate or
reduced rate contributions payable by Class 2 insured persons; and
(c) long-term care contributions
payable by insured persons. [12]
(3) There
shall also be paid into the Social Security Fund, out of monies provided by the
States, such amounts as are determined in accordance with Article 9A, for
the purpose of contributing to the cost of supplementing contributions in
accordance with Article 9.[13]
(4) There is no obligation under paragraph (3)
to pay into the Social Security Fund an amount for the year 2020.[14]
5 Class 1 contributions
(1) [15]
(2) [16]
(3) Subject
to the provisions of this Law, where in any contribution month earnings are
paid to or in respect of an employed person in respect of any one employment of
the person being an employed person’s employment and –
(a) the person is over school
leaving age; and
(b) the person has been employed
for more than a prescribed number of hours in a prescribed period,
there shall be payable
(except as provided by this Law, without regard to any other payment of
earnings to or for the benefit of the employed person in respect of any other
employment) a primary and a secondary Class 1 contribution.
(4) Subject
to the provisions of any Order made under Article 11(d), the amounts of
primary and secondary Class 1 contributions shall be determined in
accordance with Schedule 1A.[17]
6 Persons to be treated as
employers
In relation to persons
who work under the general control or management of a person other than their
immediate employer, and in relation to any other cases for which it appears to
the Minister that special provision is needed, provision may be made by Order
that for the purposes of this Law the prescribed person shall be treated as
their employer.
7 Methods of paying Class
1 contributions
(1) Except
where provision is otherwise made by Order, an employer liable to pay a
secondary Class 1 contribution in respect of a person employed by the employer
shall be liable to pay also that employed person’s primary Class 1 contribution
on behalf of that employed person, and, for the purposes of this Law,
contributions paid by the employer on behalf of an employed person shall be
deemed to be contributions paid by that employed person.
(2) Notwithstanding
any contract to the contrary, an employer shall not be entitled to make, from
earnings paid by the employer, any deduction in respect of the employer’s own
or any other person’s secondary Class 1 contributions, or otherwise to recover
such contributions from any employed person to whom the employer pays earnings;
and an employer who contravenes or attempts to contravene the provisions of
this paragraph shall be liable to a fine not exceeding level 2 on the standard
scale.[18]
(3) An
employer shall be entitled, subject to and in accordance with any Order, to
recover from an employed person the amount of any primary Class 1 contribution
paid or to be paid by the employer on behalf of the employed person; and
notwithstanding anything in any enactment, any Order under this paragraph shall
provide for recovery to be made by deduction from the employed person’s earnings,
and for it not to be made in any other way.
8 Class 2 contributions
(1) Class 2
insured persons, who are not entitled by virtue of paragraph (2), or being
so entitled do not apply, to pay reduced rate Class 2 contributions, shall
be liable to pay full rate Class 2 contributions.[19]
(2) Reduced
rate Class 2 contributions shall be payable monthly or weekly by Class 2
insured persons who apply to do so and who satisfy such conditions as may be
prescribed in relation to income and classification.[20]
(3) Subject to the provisions of any Order made
under Article 11(d), the amounts of full rate Class 2 contributions
and reduced rate Class 2 contributions payable in any month shall be
determined in accordance with Schedule 1B.[21]
8AA LTC contributions[22]
(1) An insured person’s liability to pay LTC
contributions is subject to any Order.
(2) The amount of an insured person’s LTC
contribution shall be determined in accordance with Schedule 1C.
(3) An insured person shall pay LTC
contributions in accordance with Schedule 1D and the 1961 Law as
modified by Article 49B of that Law.
(4) The liability to pay LTC contributions
commences on 1st January 2015.
8AB Method of paying employee’s
LTC contributions[23]
(1) An employer who is liable, under Article 41B
of the 1961 Law, to deduct tax from earnings payable by the employer to an
employee who is an insured person shall also be liable to pay instalments of
the employee’s LTC contribution on behalf of that employee in accordance with
Schedule 1D and the said Article 41B as modified by Article 49B
of that Law.
(2) For the purposes of this Law, contributions
paid by the employer on behalf of an employee under this Article shall be
deemed to be LTC contributions paid by the employee.
(3) An employer shall be entitled, subject to and
in accordance with Schedule 1D, to recover from an employee the amount of
any employee’s LTC contribution paid or to be paid by the employer on behalf of
the employee.
(4) The liability to pay instalments under this
Article commences on 1st January 2015.
(5) In this Article, “employee” and “employer”
have the same meaning as in Article A15 of the 1961 Law.
8AC Method of paying
sub-contractor’s LTC contributions[24]
(1) A building contractor who is liable, under
Article 41E of the 1961 Law, to deduct tax from payments made to a
sub-contractor who is an insured person or to a person nominated by the
sub-contractor for the purpose shall also be liable to pay instalments of the
sub-contractor’s LTC contribution on behalf of the sub-contractor in accordance
with Schedule 1D and Article 41E as modified by Article 49B of
that Law.
(2) For the purposes of this Law, contributions
paid by the building contractor on behalf of a sub-contractor under this
Article shall be deemed to be LTC contributions paid by that sub-contractor.
(3) A building contractor shall be entitled,
subject to and in accordance with Schedule 1D, to recover from a
sub-contractor, or from a person nominated by the sub-contractor to receive
payments for the sub-contractor, the amount of any LTC contribution paid or to
be paid by the building contractor on behalf of the sub-contractor.
(4) The liability to pay instalments under this
Article commences on 1st January 2015.
(5) In this Article, “building contractor” and “sub-contractor”
have the same meaning as in Article A15 of the 1961 Law.
8A Full contribution record
and contribution factors[25]
(1) For the purposes of this Law, a
contribution factor of 1.00 in relation to any period shall indicate a full
contribution record for that period.
(2) For the purposes of this Law, subject to
paragraph (3) and any Order, the monthly contribution factor for a person
is the sum of the contributions paid into, credited to and supplemented from
the Social Security Fund in respect of the person for the month, divided by the
standard contribution for the month that applies in the person’s case.
(3) The monthly contribution factor for a
person shall not exceed 1.00.
(4) For the purposes of this Law, subject to
any Order, the quarterly contribution factor for a person is the sum of the
monthly contribution factors for the person for each month in the quarter,
divided by 3.
(5) For the purposes of this Law, subject to
any Order, the annual contribution factor for a person is the sum of the
quarterly contribution factors for the person for each quarter in the year,
divided by 4.
(6) For the purposes of this Law, subject to
any Order, the life average contribution factor for a person is the sum of the
annual contribution factors for the person for the period described in
paragraph (7), divided by the number of contribution years specified in
the person’s case in Schedule 1AA.[26]
(7) The period referred to in paragraph (6)
is the period or periods in the aggregate, not exceeding the number of
contribution years specified in the person’s case in Schedule 1AA, for
which contributions have been paid into, credited to or supplemented from the
Social Security Fund in respect of the person and which –
(a) begins on or after the
first day of the month in which the person attains the age of 18 years;
and
(b) ends on or before the
last day of the month before the one in which the person attains pensionable
age.[27]
(8) Where contribution factors are calculated
under this Article for the purposes of determining a contribution factor for a
person, the following contributions shall be disregarded –
(a) contributions which are
not paid on their due dates and are not treated in accordance with any Order as
so paid for the purposes of survivor’s benefit, incapacity pension and old age
pension;
(b) contributions credited
only for purposes other than the purposes of survivor’s benefit, incapacity
pension and old age pension; and
(c) any other prescribed
contribution, in the case prescribed.
(9) The product of the calculation specified in
paragraph (2), (4), (5) or (6) shall be rounded up to the third
decimal place.
9 Supplementation of
contributions
(1) Subject
to the provisions of this Law, monthly contributions in respect of an insured
person shall be supplemented out of the Social Security Fund –
(a) in
the case of a Class 1 insured person, in the circumstances and by the
amount provided by paragraph 4 of Schedule 1A; and
(b) in
the case of a Class 2 insured person, in the circumstances and by the
amount provided by paragraph 5 of Schedule 1B.[28]
(2) [29]
(3) [30]
(4) Provision may be made by
Order for disqualifying a person for receiving supplementation of the person’s
contributions in accordance with paragraph (1) where the person has
intentionally arranged his or her affairs so as to entitle himself or herself
to such supplementation.[31]
9A Contributions by States to supplementation[32]
(1) The
amount required by Article 4(3) to be paid into the Social Security Fund must be determined in
accordance with this Article.[33]
(2) The
amount to be paid for each year shall be the product of the following
formula –
(A – 0.8B) x (1 + C)2
Where –
(a) A
is the total amount required, for the base year, for the purpose of
supplementing contributions in accordance with Article 9, reported in the
accounts prepared in accordance with Article 30(4);
(b) B is the aggregate of the following amounts, as they
are reported in the accounts prepared in accordance with Article 30(4) –
(i) the
Class 1 secondary
contributions paid for the base year in accordance with paragraph 3(2)(c)
of Schedule 1A,
(ii) the
full rate Class 2
contributions paid for the base year in accordance with paragraph 3(c) of
Schedule 1B, and
(iii) the reduced rate Class 2 contributions paid for the base
year in accordance with paragraph 4(c) of Schedule 1B; and
(c) C is
the percentage rise or fall in the Jersey Index of Earnings in the base year.[34]
(3) If 0.8B is equal to or greater than A, no money is
required to be paid for the year.[35]
(4) Despite paragraphs (2) and (3) –
(a) no annual amount is to be
paid for the year 2021; and
(b) the
annual amount to be paid for the year 2022
is £76,140,000.[36]
(4A) [37]
(5) The
amount to be paid under this Article for a year may be paid in a lump sum or in
instalments, and at such time or times, as the Minister determines.
(6) In this Article, “base year” means the year that is 2 years
before the year for which the amount to be paid into the Social Security Fund
is being determined.[38]
10 Exceptions from liability
and crediting of contributions
(1) Provision
may be made by Order for excepting insured persons otherwise liable for
contributions of any class from such liability for such periods and in such
circumstances as may be prescribed.
(2) An
Order made under paragraph (1) shall not except a person from liability to
pay contributions otherwise than on his or her own application, but may provide
for so excepting a person with effect from the day the person’s application is made or a day that is earlier or
later than that day.[39]
(3) Provision
may be made by Order for the crediting of contributions of any class to an
insured person for the purpose of safeguarding future entitlement to benefit
(whether his or her own or another person’s entitlement) but not so as to cause
so much
of his or her contributions as are payable into the Social Security Fund to
exceed the standard contribution.[40]
11 General contribution
provisions
Provision may be made by
Order –
(a) for
treating, for the purpose of any right to benefit, contributions paid after the
due dates as paid on those dates or on such later dates as may be prescribed or
as not having been paid, and for treating, for the purpose aforesaid,
contributions payable by an employer, but not paid, as paid where the failure
to pay is shown not to have been with the consent or connivance of, or
attributable to any negligence on the part of, the relevant employed person,
and in the case of contributions so treated, for treating them also as paid at
a prescribed time or in respect of a prescribed period;
(b) for
treating earnings not paid at normal intervals as paid at such intervals as may
be prescribed;
(c) for
the collection or aggregation of Class 1 contributions or LTC contributions
where a person is employed in more than one employment;
(d) for
calculating or otherwise adjusting the amount of a contribution payable
according to a prescribed scale or figure so as to avoid fractional amounts or
otherwise facilitate computation;
(da) for
calculating or otherwise adjusting any amount determined, in accordance with
this Law, by reference to any index or scale, so as to avoid fractional amounts
or otherwise facilitate computation;
(e) for
securing that liability for the payment of contributions is not avoided or
reduced by means of irregular or unequal payments of earnings or by a person
following, in the payment of earnings, any practice which is abnormal for the
employment in respect of which the earnings are paid;
(f) that,
for the purpose of determining whether a contribution is payable in respect of
any person, that person shall be treated as having attained at the beginning of
a contribution month, or as not having attained until the end of the
contribution month, any age which the person attains during the course of that
month;
(g) for
the return of contributions under this Law paid in error or in such other
circumstances as may be prescribed;
(ga) for
the correction of overpayments or underpayments of contribution made in such
circumstances as may be prescribed;
(h) for
requiring persons to maintain, in such form and manner as may be prescribed,
records –
(i) of the earnings paid by
them to and in respect of employees, and
(ii) of the contributions paid
or payable in respect of earnings so paid,
for the purpose of
enabling the incidence of liability for contributions of any class to be determined,
and to retain the records for so long as may be prescribed;
(ha) for
prescribing circumstances in which the earnings of any employed person may be
treated as being of such an amount, not exceeding any earnings limit specified
in Schedule 1A or 1B, as the Minister considers appropriate;
(hb) for
prescribing circumstances in which the income of any person may be treated as
being of such amount, not exceeding any income limit specified in Schedule 1C,
as the Minister considers appropriate;
(j) for
any other matters incidental to the payment, collection or return of
contributions. [41]
PART 3
BENEFIT
12 Description of benefits[42]
Benefit shall be of the following descriptions –
(a) incapacity benefit, which shall consist of
short term incapacity allowance, long term incapacity allowance and incapacity
pension;
(b) parental benefit, consisting of parental
grant and parental allowance;
(d) survivor’s benefit, which shall consist of
survivor’s allowance and survivor’s pension;
(e) old age pension;
(ea) 2013 old age pension adjustment;
(f) death grant;
(g) insolvency benefit;
(h) home carer’s allowance.
13 Rates and amounts of
benefit
(1) Subject
to the provisions of this Law –
(a) the weekly rates of
benefits and the amounts of any single payment benefits (apart from long term
incapacity allowance and insolvency benefit) are the amounts set out in
Schedule 1;
(b) the weekly rate of long
term incapacity allowance shall be the percentage of the standard rate of
benefit in which the degree of incapacitation, assessed in accordance with the
provisions of Article 16, is expressed; and
(c) the amount of insolvency
benefit shall be calculated in accordance with Articles 26A to 26H.[43]
(2) The
standard rate of benefit for the purposes of this Law (except for the purposes
of the old age pension) shall, on the appointed day, be an amount equal to the
standard weekly rate of parish welfare payable for a single householder on the
appointed day and thereafter shall be increased on the first day of October in
every year by the percentage figure equal to the percentage rise in the Jersey
Index of Earnings during the 12 months commencing July of the preceding
year.[44]
(3) Provision
may be made by Order for –
(a) calculating daily,
monthly and yearly equivalents of the weekly standard rate of benefit;
(b) calculating or otherwise
adjusting the amount of any benefit so as to avoid fractional amounts or
otherwise facilitate computation.
14 Contribution conditions
(1) The
contribution conditions for the several descriptions of benefit (other than
insolvency benefit or the 2013 old age pension adjustment) shall be
as set out in Schedule 2.[45]
(2) Provision
may be made by Order for the entitling to incapacity benefit, home carer’s
allowance, parental allowance, survivor’s benefit and old age pension of
persons who would be so entitled but for the fact that the relevant
contribution conditions set out in paragraphs 1(1)(b), 2(1)(b), 3(1)(b),
3A(1)(b), 4(1)(b) and 6(1)(b) of Schedule 2 are not satisfied.[46]
(3) Any
Order made under paragraph (2) shall provide that benefit payable by
virtue of the Order shall be payable at a rate, or shall be of an amount, less
than that specified in Schedule 1, and the rate or amount prescribed by
the Order may vary with the extent to which contribution conditions are
satisfied.
(4) [47]
15 Short term incapacity
allowance[48]
(1) Subject
to the provisions of this Law, a person who –
(a) is under pensionable age
on any day for which benefit is claimed;
(b) is not entitled to a
reduced old age pension under Article 25(1A); and
(c) satisfies the relevant
contribution conditions,
shall be entitled to short
term incapacity allowance in respect of any day of incapacity for work during a
period of incapacity for work.
(2) Where
in respect of any period of incapacity for work a person has been entitled to
short term incapacity allowance for 364 days (including, in the case of a
woman, any day for which she was entitled to a parental allowance), he or she
shall cease to be entitled to that benefit for any subsequent period of
incapacity for work falling within that period.[49]
(3) A
person shall not be entitled to short term incapacity allowance –
(a) for any period in which
he or she works; or
(b) in respect of any disease
or injury for which he or she is entitled to long term incapacity allowance.[50]
(4) Subject
to the provisions of this Law, where a person who is under pensionable age and
is not entitled to a reduced old age pension under Article 25(1A) ceases
by virtue of paragraph (2) of this Article to be entitled to short term
incapacity allowance –
(a) if he or she satisfies
the requirements of Article 16, he or she shall be entitled to long term
incapacity allowance; or
(b) if he or she satisfies
the requirements of Article 17, he or she shall be entitled to an
incapacity pension.
16 Long term incapacity
allowance[51]
(1) Subject
to the provisions of this Law, a person who –
(a) is under pensionable age;
(b) is not entitled to a
reduced old age pension under Article 25(1A);
(c) as a result of the
relevant disease or injury is suffering from a loss of physical or mental
faculty which is likely to be permanent; and
(d) satisfies the relevant
contribution conditions,
shall be entitled to long
term incapacity allowance.
(2) The
assessment of a claimant’s incapacitation for the purposes of long term
incapacity allowance –
(a) shall be made by a
medical board appointed under Article 34AA, in accordance with –
(i) this Article,
(ii) the provisions of any
Order made under this Article or Article 34AA, and
(iii) Article 34A; and
(b) shall take into account
any period (as to the commencement and duration of which further provision may
be made by Order) during which the claimant has suffered and may be expected to
continue to suffer from loss of faculty resulting in such incapacitation.[52]
(3) If
the claimant is receiving or has received short term incapacity allowance in
respect of the relevant disease or injury, the period to be taken into account
under paragraph (2) shall not begin earlier than the end of the last
period during which he or she received that allowance.
(4) [53]
(5) The
assessment shall specify –
(a) as a percentage, the
degree of incapacitation resulting from the loss of faculty; and
(b) the period taken into
account by the assessment.[54]
(6) In
the assessment of a claimant’s incapacitation –
(a) the percentage and the
period to which paragraph (5) refers shall not be specified more
particularly than is necessary for the purpose of determining the claimant’s
rights in relation to long term incapacity allowance;
(b) if the percentage so
specified is lower than 5%, the claimant shall not be entitled to long term
incapacity allowance in respect of that incapacitation; and
(c) a percentage which is
higher than 5% but is not a multiple of 5 shall be treated as being the next
highest percentage which is a multiple of 5.
(7) Subject
to the other provisions of this Article, provision may be made by Order for the
definition of the principles on which incapacitation is to be assessed.[55]
(8) Any
such Order may in particular prescribe that a specified loss of faculty shall
be treated as resulting in a specified percentage of incapacitation.[56]
17 Incapacity pension[57]
(1) Subject
to the provisions of this Law, a person who –
(a) is under pensionable age;
(b) is not entitled to a
reduced old age pension under Article 25(1A);
(c) as a result of the
relevant disease or injury is likely to be permanently incapable of work; and
(d) satisfies the relevant contribution
conditions,
shall be entitled to an
incapacity pension.
(2) An
incapacity pension shall be payable until the beneficiary becomes entitled to a
reduced old age pension under Article 25(1A) or attains pensionable age,
whichever event occurs first.
(3) The
amount of the incapacity pension to which a beneficiary is entitled shall be
calculated as if, in addition to any other contributions paid by the
beneficiary and on his or her behalf, the contributions which would be payable
by or credited to the beneficiary and on his or her behalf had been paid or
credited from the date from which the beneficiary became entitled to the
incapacity pension until the end of the month before the one in which he or she
would attain pensionable age.
(4) An
incapacity pension shall cease to be payable if the beneficiary works but if
the beneficiary subsequently ceases to work and satisfies the requirements in
paragraph (1) he or she shall again be entitled, from the date on which he
or she so ceases work, to an incapacity pension in accordance with this
Article.
18 General provisions
concerning incapacity benefit[58]
(1) For
the purposes of any provisions of this Law relating to incapacity
benefit –
(a) any 2 days of incapacity
for work (whether consecutive or not) within a period of 7 consecutive days
shall be treated as one period of incapacity for work; and
(b) any 2 such periods which
are not separated by a period of more than 13 weeks shall be treated as one
period of incapacity for work.
(2) Provision
may be made by Order for all or any of the following matters relating to
incapacity benefit –
(a) the defining of days
which are or are not to be treated as days of incapacity for work;
(b) the disqualifying of a
person for the receiving of incapacity benefit, for such period not exceeding
13 weeks as may be determined in such manner as may be prescribed, if –
(i) the relevant disease or injury is
attributable to his or her own wilful act,
(ii) he or she behaves in a
manner calculated to retard his or her recovery;
(iii) he or she fails without
good cause to attend for or to submit himself or herself to such medical or
other examination or treatment as may be required in accordance with the Order,
or to observe any prescribed rules of behaviour; or
(iv) he or she is guilty of
obstruction or misconduct in connection with any relevant medical examination
or treatment;
(c) the requiring of a
claimant for or beneficiary in receipt of incapacity benefit –
(i) to submit from time to time to medical
examination for the purpose of determining the effect of the relevant disease
or injury, or the appropriate treatment for it, and
(ii) to submit from time to
time to appropriate medical treatment for that disease or injury;
(d) the imposing in the case
of any class of persons of additional conditions with respect to the receipt of
incapacity benefit and restrictions on the rate and duration of the benefit if,
having regard to special circumstances, it appears to the Minister necessary to
do so for the purpose of preventing inequalities or injustice to the general
body of insured persons.[59]
(3) Any
Order made under this Article requiring persons to submit to medical
examination or treatment may direct that they are to attend for that purpose at
such times and places as may be required by persons specified in the Order.[60]
(4) Where
it appears to the Minister that a question has arisen whether an assessment of
incapacity benefit ought to be revised, the Minister may direct that payment of
the benefit shall be suspended in whole or in part until that question has been
determined.
(5) Without
prejudice to paragraphs (2) and (4), provision may be made by Order for
all or any of the following matters relating to long term incapacity
allowance –
(a) the period for which, and
grounds on which, any award of long term incapacity allowance may be backdated;
and
(b) the calculation of the
amount of any backdated award such as is mentioned in sub-paragraph (a).[61]
18A Home carer’s allowance[62]
(1) Subject
to the provisions of this Law, a person (the “carer”) shall be entitled to a
home carer’s allowance for any day on which –
(a) he or she is regularly
and substantially engaged in caring for another person (the “cared for person”);
and
(b) the conditions in
paragraphs (2) and (3) are satisfied.
(2) The
carer must –
(a) satisfy such conditions
as to residency and presence in Jersey as may be prescribed;
(b) satisfy the relevant
contribution conditions;
(c) not have earnings, for
any prescribed period, that exceed such amount as may be prescribed; and
(d) not receive earnings for
the provision of such care to the cared for person.
(3) The
cared for person must –
(a) meet the criteria for –
(i) the rate payable in respect of the
personal care element of the impairment component under paragraph 6(3)(c)
of Schedule 1 to the Income Support
(Jersey) Regulations 2007, or
(ii) being assessed as being
in need of long-term care under Article 5(1) of the Long-Term Care (Jersey)
Law 2012; and
(b) satisfy such conditions
as to residency and presence in Jersey as may be prescribed.[63]
(4) A
carer who has attained pensionable age shall not be entitled to a home carer’s
allowance in respect of a cared for person unless the carer –
(a) was entitled to such
allowance in respect of the cared for person (or is treated by Order as having
been so entitled) immediately before attaining that age; and
(b) claimed such allowance
before attaining that age.
(5) A
carer shall not be entitled for the same day to more than one home carer’s
allowance.
(6) Where,
apart from this paragraph, 2 or more carers would be entitled for the same day
to home carer’s allowance in respect of the same cared for person, one of them
only shall be entitled as determined in the prescribed manner.
(7) The
Minister –
(a) shall prescribe, for the
purposes of paragraph (1)(a), the circumstances in which a carer is to be
treated as regularly and substantially engaged in caring for a cared for
person; and
(b) may prescribe earnings
that are to be disregarded for the purposes of paragraph (2)(c) or (d).
21 Entitlement to parental
grant[64]
(1) Subject to the provisions of this Law, a
person to whom paragraph (2) applies is entitled to a parental grant upon
the birth or adoption of a child.
(2) This paragraph applies to a person
who –
(a) is
a parent of the child; and
(b) satisfies
the relevant contribution conditions, and any prescribed requirements.
(3) In respect of any one child –
(a) only
one person may receive payment of the parental grant; but
(b) where
more than one person is entitled to parental grant, the grant must be paid, in
the following order of priority –
(i) to
the person who is nominated by the other persons so entitled, in such manner as
may be prescribed, as the parent to whom the grant is to be paid,
(ii) if
no person is nominated, and except in a case of adoption, to the birth mother,
or
(iii) to
the person whose name appears first on the birth certificate or adoption
certificate.
(4) If all persons entitled to the grant have
died, the parental grant may be paid to such other person as may be prescribed.
(5) No more than one parental grant is to be
paid in respect of any one child, but subject to any provision which may be
made by Order, a person is entitled to a parental grant in respect of each
child –
(a) in
a case of the birth of more than one child as a result of the same pregnancy;
or
(b) in
the case of –
(i) an
adoption, by the placement for adoption of more than one child, or
(ii) an
overseas adoption, by more than one child being adopted,
as part of the same arrangement.
(6) Further provision may be made by Order for
the purpose of giving full effect to this Article, and in particular as
to –
(a) the
application of this Article, with or without modification, in relation to a
person or class of persons, including a person who is entitled to a parental
grant and who requests, in such a manner as may be prescribed, that the
parental grant is to be paid prior to the expected date of birth or placement
for adoption, as the case may be;
(b) the
time and manner of payment of parental grant;
(c) the
determination of any dispute between persons regarding the nomination under
paragraph (3)(b).
22 Entitlement to parental
allowance[65]
(1) Subject to the provisions of this Law, a
person to whom paragraph (2) applies is entitled to parental
allowance –
(a) in
the case of a host mother, in accordance with paragraph (3); and
(b) in
the case of a parent, in accordance with paragraphs (4) to (9).
(2) This paragraph applies to a person
who –
(a) is
a parent, or the host mother, of a child; and
(b) satisfies
the relevant contribution conditions, and any prescribed requirements.
(3) The host mother of a child is entitled to
parental allowance –
(a) irrespective
of any other payment of parental allowance to any other person for any period;
but
(b) for
the post-natal period only, and for no other period.
(4) In respect of any one adoption or birth,
the period for which parental allowance is to be paid must not exceed a total
of 32 weeks, but that total –
(a) is
in addition and without prejudice to any entitlement of a host mother under
paragraph (3), in respect of the post-natal period; and
(b) applies
without regard to the number of children adopted or born, or of persons
entitled to the allowance.
(5) The total number of weeks mentioned in
paragraph (4) must fall within the period –
(a) beginning
no earlier than the date which is 11 weeks prior to the expected adoption
date or date of birth; and
(b) ending –
(i) in
the case of adoption, on the day which is 2 years after the date of
adoption, or
(ii) in
any other case, on the day which is the child’s second birthday.
(6) Where one parent entitled to parental
allowance is the birth mother, payment of parental allowance must be made to
the birth mother for the post-natal period.
(7) Where a person entitled to parental
allowance is also a parent exercising a right to paid parental leave under
Article 55E of the Employment (Jersey) Law 2003, parental allowance must be
paid for each week of paid parental leave taken by that person.
(8) No more than 2 parents are entitled to
receive payment of parental allowance in respect of any one adoption or birth, but
where 2 parents are so entitled, they –
(a) must
nominate, subject to paragraphs (6) and (7) and in such manner as may be
prescribed, the parent to whom a parental allowance is to be paid; and
(b) may
specify, subject to paragraph (9) and in such manner as may be prescribed,
the period of weeks for which the allowance is to be paid to a nominated
parent.
(9) Periods specified under paragraph (8)(b)
need not be continuous, but –
(a) no
more than 3 separate periods may be specified for each nominated parent;
and
(b) each
specified period must be of no less than 2 weeks.
(10) Further provision may be made by Order for
the purpose of giving full effect to this Article, and in particular as
to –
(a) the
determination of any dispute between persons regarding the nomination to be
made under paragraph (8)(a);
(b) determination
of an issue or dispute regarding entitlement to parental allowance, or the
period for which or the parent to whom it is payable;
(c) cases
in which particular contribution conditions may be disapplied;
(d) requirements
which must be satisfied for the purpose of making a valid claim to parental
allowance;
(e) cases
in which persons may be disqualified from receiving parental allowance;
(f) cases
in which the period for which parental allowance is payable may be varied, and
variations of that period;
(g) entitlement
to, and payment of, parental allowance in a case where no nomination is made
under paragraph (8)(a);
(h) entitlement
to, and payment of, parental allowance in a case where a parent is no longer
alive;
(i) the
time and manner of payment of parental allowance.
23 Interpretation of
Articles 21 and 22[66]
(1) In Articles 21, 22 and paragraph (2),
references to adoption, the adoption date, overseas adoption and surrogacy are
to be construed, subject to paragraph (2), in accordance with
Article 55A (interpretation for the purposes of Part 5A) of the Employment (Jersey) Law 2003.
(2) For the purposes of Articles 21 and
22 –
“adoption certificate” means a certified copy, issued under
Article 60(2) of the Marriage and Civil Status (Jersey) Law 2001, of an adoption
registration under that Law;
“birth” includes, except where the context otherwise requires –
(a) the
birth of a living child at the full term of pregnancy, and
(b) the
birth of a child, whether living or stillborn, at any time after 24 weeks
of pregnancy;
“birth certificate” means a short form birth certificate, issued
under Article 60(1) of the Marriage and Civil Status (Jersey) Law 2001, relating to a birth
registration under that Law;
“birth mother” means a woman who gives birth to a child, but does
not include a host mother;
“host mother” means a woman who gives birth to a child, in the case
where the child is or is to be placed with a surrogate parent;
“parent” means a person, other than a host mother, who –
(a) is,
or is to be –
(i) named
on the birth certificate or adoption certificate of a child, or
(ii) a
surrogate parent; and
(b) has,
or expects to have, responsibility for the upbringing of the child or the main
responsibility (apart from any responsibility of the birth mother) for the
upbringing of the child;
“post-natal period” means the continuous period of 6 weeks
beginning with the day on which birth occurs.
(3) For the purposes of paragraph (1), a
person is treated as having responsibility, or the main responsibility, for the
upbringing of a child, if the person would have had such responsibility but for
the fact that the child was stillborn after 24 weeks of pregnancy, or has
died.
24 Survivor’s benefit[67]
(1) Subject
to the provisions of this Law, where a person who dies (the “deceased”) is, at
the time of his or her death, married or a civil partner, the spouse or civil
partner who survives him or her (the “survivor”) shall be entitled to
survivor’s benefit if the deceased satisfied the relevant contribution
conditions, and –
(a) in the case of survivor’s
allowance, at the time of the death of the deceased, either the deceased or the
survivor was not entitled to an old age pension, or was under pensionable age;
or
(b) in the case of survivor’s
pension, at the expiry of 52 weeks following the death of the deceased,
the survivor –
(i) has not, since the death of the deceased,
married or formed a civil partnership,
(ii) is under pensionable
age,
(iii) is not entitled to a
reduced old age pension under Article 25(1A), and
(iv) has a dependent child.
(2) Subject
to paragraphs (4) and (6), survivor’s allowance shall be payable to a
survivor for the 52 weeks following the death of the deceased.
(3) Subject
to paragraphs (4), (5) and (6), survivor’s pension shall be payable to a
survivor from the expiry of 52 weeks following the death of the deceased
until the survivor becomes entitled to a reduced old age pension under Article 25(1A)
or attains pensionable age.
(4) A
survivor shall cease to be entitled to survivor’s benefit if he or she marries
or forms a civil partnership.
(5) A
survivor shall cease to be entitled to survivor’s pension when every child who
was a dependent child at the time described in paragraph (1)(b) has ceased
to be a dependent child.
(6) Survivor’s
benefit shall not be payable to a survivor in respect of any period when the
survivor is in a relationship with another person that is like marriage or
civil partnership.
(7) For
the purposes of this Article, “dependent child” means a child who is –
(a) the natural or adopted
child of the deceased or the survivor;
(b) under the age of 25; and
(c) living with the survivor
as part of his or her household.
25 Old age pensions
(1) Subject
to the provisions of this Law a person shall be entitled to an old age pension
if –
(a) the person is over
pensionable age; and
(b) the person satisfies the
relevant contribution conditions.
(1A) Subject
to the provisions of this Law, a person shall be entitled to a reduced old age
pension if –
(a) the person is over the
reduced pension age specified in the person’s case in Schedule 1AA;
(b) the person satisfies the
relevant contribution conditions; and
(c) the person elects, in the
prescribed manner, to take a reduced old age pension under this paragraph.[68]
(1B) An
election under paragraph (1A) shall be irrevocable, and a person who
becomes entitled to a reduced old age pension under that paragraph shall not be
entitled to any increase in that pension by reason of subsequently attaining
pensionable age.[69]
(2) Subject
to the provisions of this Law, an old age pension (whether or not it is a
reduced pension) shall be payable from the date on which the person becomes
entitled to it, and shall be payable for life.[70]
(3) Subject
to the provisions of this Law, a woman over pensionable age shall be entitled
to an old age pension by virtue of the insurance of her husband, being a husband –
(a) to whom she is married at
the time when she attains that age;
(b) in respect of whose death
she was immediately before attaining that age entitled to survivor’s benefit;
or
(c) whom she has married
after attaining that age,
if the following
conditions are satisfied, that is to say –
(i) either that he is over
pensionable age or that he is dead; and
(ii) that he satisfies the
relevant contribution conditions. [71]
(4) Subject
to the provisions of this Law, an old age pension payable to a woman by virtue
of her husband’s insurance shall commence from the date on which the provisions
of paragraph (3) are satisfied in relation to the pension and shall be
payable for life:
Provided that, if a widow
entitled to an old age pension by virtue of her late husband’s insurance
remarries or enters into civil partnership, the pension shall not be payable
for any subsequent period.[72]
(5) A
woman shall not be entitled for the same period to more than one old age
pension, but if she would be so entitled but for this provision, she may, on
such occasions and in such manner as may be prescribed, choose which she shall
be entitled to.
(6) Where
immediately before attaining pensionable age a woman is a widow not entitled to
survivor’s benefit, she may elect that, in calculating for the purpose of her
right to an old age pension by virtue of her own insurance the life average of her
contribution factors, there shall be treated as paid or credited either –
(a) for each contribution
year falling wholly or partly before her husband’s death; or
(b) for each contribution
year falling wholly or partly during the period of their marriage,
contributions equal to the
life average (ascertained as at the date of his attaining pensionable age or
dying under that age) of his contribution factors instead of the contributions
actually paid or credited to her for that year.[73]
(7) Notwithstanding
the foregoing provisions of this Article, and subject to any prescribed
conditions, provision shall be made by Order for entitling a woman who was an
insured person under the Law of 1950 to an old age pension by virtue of her
own insurance on attaining the age of 60.
25A 2013 old age pension
adjustment[74]
(1) A
person shall be entitled to the 2013 old age pension adjustment
if –
(a) on the prescribed date,
the person is eligible for an old age pension or reduced old age pension; and
(b) in accordance with the
Law and any Order made under it, has applied for and, in the case of a reduced
old age pension, elected to take, such pension.
(2) The
Minister shall by Order prescribe –
(a) a date for the purposes
of paragraph (1)(a); and
(b) an amount for the
purposes of paragraph 3 of Part 2 of Schedule 1.
26 Death grant
(1) Subject
to the provisions of this Law, a death grant shall be payable in respect of the
death of any person (in this Article referred to as the “deceased”) if the
deceased either himself or herself satisfied the relevant contribution
conditions, or was at death the husband, wife, civil partner, widower, widow or
a child of the family, of a person satisfying the said conditions, or a child
who –
(a) had, immediately before
the death of some other person satisfying the said conditions, been a child of
the family of that other person; or
(b) was a posthumous son or
daughter of a man satisfying the said conditions.[75]
(2) Notwithstanding
the provisions of paragraph (1), provision may be made by Order for a
death grant to be payable if the relevant contribution conditions were
satisfied by such other person as may be prescribed.
(3) Except
where provision is otherwise made by Order, a death grant shall not be payable
in respect of a death occurring outside Jersey.
26A Qualifying for insolvency benefit[76]
(1) A
person qualifies under this Article if all of the following conditions are
satisfied –
(a) the person was in
employment as, within the meaning of the Employment (Jersey)
Law 2003, an employee of an employer;
(b) the person was so employed
wholly or mainly in Jersey;
(c) the employer is bankrupt;
(d) that bankruptcy is the
principal reason for the fact that the person is no longer so employed;
(e) the employer was liable
to pay Class 1 contributions, in respect of the employee and the employment,
in any one or more contribution months that fell within the period of 3 months
that ended when the employer became bankrupt;
(f) the employer has not
paid the employee in full the amounts specified in Article 26C as they
relate to that employee and that employment.
(2) In
this Article and Article 26C, “bankruptcy” in relation to an employer
includes any form of insolvency that results in an inability on the part of the
employer to continue trading or to continue performing the employer’s activities,
being insolvency that –
(a) has occurred in Jersey or
elsewhere; and
(b) has resulted in the
employer’s going into administration (however expressed), liquidation (however
expressed) or receivership (however expressed) in Jersey or elsewhere or
entering in Jersey or elsewhere into an arrangement (however expressed) with
the employer’s creditors.
(3) For
the purposes of this Article, it does not matter whether an employer’s trading
or activities took place in Jersey or elsewhere.
26B Insolvency benefit and
deductions[77]
A person who qualifies
under Article 26A shall be entitled to an insolvency benefit calculated by
firstly adding the components referred to in Article 26C, secondly making
the deductions (if any) specified in Articles 26F and 26G and finally
applying the discounts (if any) under Article 26D.
26C Components of insolvency benefit[78]
(1) A
component of the insolvency benefit shall be any unpaid amount of wages (where “wages”
has the same meaning as in the Employment (Jersey)
Law 2003) that relate to the person’s service in employment by the
relevant employer during the 12 months that ended with the cessation of
that service.
(2) The
components of the insolvency benefit shall also include any unpaid amounts that
relate to the person’s employment by the relevant employer and are payable to
the person (or would have been payable to the person except for the fact that
the person was dismissed by virtue of the order of a court, being an order
relating to the bankruptcy or winding up of the employer) as follows –
(a) subject to Article 26E,
an amount in lieu of a period of notice of termination of that employment,
where the amount is in accordance with Part 6 of the Employment (Jersey)
Law 2003;
(b) an amount of redundancy
payment in respect of that employment, where the amount is in accordance with Part 6A
of the Employment
(Jersey) Law 2003;
(c) any amount (being an
amount not already accounted for under paragraph (1)) owing in respect of
a holiday actually taken by the person during the 12 months that ended
with the cessation of the person’s service in that employment;
(d) any amount (being an
amount not already accounted for under paragraph (1) or sub-paragraph (c))
that –
(i) accrued as holiday pay at any time during
the 12 months that ended with the cessation of the person’s service in
that employment, and
(ii) under the person’s
contract of employment –
(A) had in those 12 months
become payable to the person in respect of the period of a holiday, or
(B) would in the ordinary
course have become payable to the person in respect of the period of a holiday
if the person’s service in that employment had continued until the person had
become entitled to a holiday.
(3) In
adding the components relating to a person under this Article, if any one
amount (or part of an amount) relates to more than one component it shall not
be counted more than once towards the sum referred to in Article 26B.
(4) Despite
anything in this Article, a component shall not be counted towards the sum
referred to in Article 26B to the extent (if any) that the Minister may
prescribe by Order.
(5) A
reference in this Article to a holiday includes annual leave and leave (if not
already included in annual leave) in respect of public holidays (including
Christmas) and bank holidays.
(6) For
the purposes of paragraph (2)(a), Part 6 of the Employment (Jersey)
Law 2003 shall be read as if any reference to notice in that Part were
to the notice that would apply under that Part in the absence of any relevant
agreement, as referred to in Article 56(7) of that Law, for a period of
notice longer than those specified in paragraphs (1) and (2) of that
Article.
(7) For
the purposes of paragraph (2)(b), Part 6A of the Employment (Jersey)
Law 2003 shall be read as if Article 60D of that Law had no
effect.
26D Cap on insolvency benefit[79]
(1) An
insolvency benefit payable to a person who qualifies under Article 26A
cannot in aggregate exceed an amount of £10,000 in respect of any one
employment of the person.
(2) If
the insolvency benefit payable to a person would (but for the operation of this
paragraph) in aggregate exceed an amount applying under paragraph (1), the
aggregate shall be discounted so that it equals that amount.
(3) The
discounting shall be applied in the following order –
(a) first to the amount of
the component referred to in Article 26C(2)(a);
(b) then to the amount of the
component referred to in Article 26C(2)(b);
(c) then to the total of the
amounts of the components referred to in Article 26C(2)(c) and (d);
(d) then to the amount of the
component referred to in Article 26C(1),
but only to such of the
components (in that order), and to such extent, as is necessary to bring the
aggregate down to the amount that applies under paragraph (1).[80]
(4) The
Minister may by Order prescribe –
(a) a different amount (or
one or more different amounts in respect of more than one employment) for the
purposes of paragraph (1); or
(b) another order in which
amounts are to be discounted under paragraph (3), or proportions in which
those amounts are to be discounted, or both such an order and such proportions.
(5) Anything
so prescribed shall apply instead of what is specified in paragraph (1) or
(3), as the case requires.
26E Pay in lieu of notice:
requirement to be looking for work[81]
(1) For
an amount referred to in Article 26C(2)(a) in lieu of a period of notice
of termination of a person’s employment to be treated as a component of insolvency
benefit, the person must have been, in that period, available for, and actively
seeking, remunerative work.
(2) In
this Article, except to the extent to which the States by Regulations otherwise
prescribe for the purposes of this Article –
“actively seeking” in
relation to a person and to work means doing all of the following –
(a) taking all reasonable
steps (including any appropriate training or work experience) to obtain
suitable work;
(b) not unreasonably turning
down any offer of suitable work; and
(c) attending every interview
with an officer of the Department of Social Security to which the person has
been invited unless the person has a reasonable excuse for not so attending;
“available for” in
relation to a person and to work has the same meaning as under Article 3
of the Income Support
(Jersey) Law 2007;
“remunerative work” has
the same meaning as under Article 3 of the Income Support (Jersey)
Law 2007.
26F Pay in lieu of notice:
deductions of certain amounts[82]
(1) The
following amounts payable to a person in respect of the whole or any part of any
period of notice to which the person is or has been entitled in respect of the
termination of the person’s employment shall be deducted from the component referred
to in Article 26C(2)(a) that relates to the person –
(a) any wages that the person
earns from employment that the person commences during that period (but not any
wages that the person earns during that period from the continuation of any
employment that –
(i) the person started before the beginning of
that period, and
(ii) is employment that the
person intended to engage in in addition to the employment that was
terminated);
(b) any benefit under this
Law in the form of short-term incapacity allowance, as referred to in Article 15;
(c) any benefit under this
Law in the form of parental allowance, as referred to in Article 22;
(d) such part of any amount
of home carer’s allowance, as referred to in Article 18A, as would not
have been payable but for the termination of the person’s employment;
(e) such part of any amount
of income support under the Income Support (Jersey)
Law 2007 as would not have been payable but for the termination of the
person’s employment;
(f) such other amounts as
the Minister may prescribe by Order.[83]
(2) The
reference in paragraph (1)(a) to wages that the person earns from
employment that the person commences during a period includes –
(a) wages to which the person
is entitled in respect of that employment during the period even if payment (in
part or in whole) of those wages occurs after the end of the period; and
(b) wages to which the person
would have been entitled in respect of that employment during the period but
for the fact that the person agreed to waive his or her entitlement to those
wages or to postpone his or her entitlement to those wages until after the end
of the period.
(3) In
this Article, “wages” has the same meaning as in the Employment (Jersey)
Law 2003.[84]
26G Other deductions[85]
(1) If
primary Class 1 contributions would have been payable in respect of any
component specified in Article 26C if that component had been paid by the
employer, their value shall be deducted from the component.
(2) If
income tax payable under the Income Tax (Jersey)
Law 1961 would have been deductible or payable in respect of any
component specified in Article 26C if that component had been paid by the
employer, its value shall be deducted from the component.
(3) Any
amount owed by the employee to the employer in respect of leave that has been
taken in excess of the employee’s entitlement, in respect of any overpayment of
wages or in respect of any other matter shall be deducted from the sum of the
components under Article 26C.
26H Components cannot be
negative[86]
The value (after any
deductions referred to in Articles 26F and 26G have been made) of a
component referred to in Article 26C, or of the sum of the components referred
to in Article 26C, cannot, for the purposes of any of Articles 26A to
26G, be less than zero.
26I Subrogation[87]
(1) The
Minister shall be entitled to be subrogated to the right of a person to recover
any amount referred to in Article 26C(1) or (2), being so entitled to the
extent to which the amount has counted towards an insolvency benefit paid to
the person.
(1A) In
relation to any insolvency benefit paid to a person, the Minister shall also be
entitled to recover the amount of any deduction of value made under Article 26G(1)
or (2).[88]
(1B) The
Minister may recover that amount from a party from whom the Minister is
entitled, pursuant to the subrogation referred to in paragraph (1), to
recover part or all of the amount of the component from which the value was so
deducted.[89]
(2) Nothing
in paragraph (1) shall prevent the person from recovering any amount
referred to in Article 26C(1) or (2) to the extent to which the amount has
not counted towards an insolvency benefit paid to the person.
(2A) Nothing
in paragraph (2) shall entitle the person to recover an amount
corresponding to any value deducted under Article 26G(1) or (2) or to
recover any amount deducted under Article 26G(3).[90]
(3) The
operation of this Article shall not be affected by the death, or any incapacity,
of the person.
(4) In
this Article and Article 26J –
“count towards” means have
a net positive effect on the amount of an insolvency benefit after any
requirement under Articles 26A to 26H to make a deduction, discount or
other treatment has been complied with;
“person” means a person
who is paid an insolvency benefit;
“recover” means recover
from the relevant employer or from another person, and otherwise than as an
insolvency benefit or as a component of an insolvency benefit.
26J Repayment where employee
recovers some amounts[91]
(1) A
person who recovers any part of an amount referred to in Article 26C(1) or
(2) shall repay the part so recovered to the Social Security Fund to the extent
to which the part has counted towards an insolvency benefit paid to the person.
(2) For
the purposes of this Article, “part” includes all and none.
27 Increase of benefit for
dependants[92]
(1) The
weekly rate of short term incapacity allowance, incapacity pension and parental
allowance shall be increased by the amount set out in the second column of Part 3
of Schedule 1, and the weekly rate of long term incapacity allowance shall
be increased by a percentage of that amount, being the percentage in which the
degree of incapacitation (assessed in accordance with the provisions of Article 16)
is expressed, for any prescribed period during which the beneficiary or any
other prescribed person is caring, in prescribed circumstances, for a person of
a prescribed category.[93]
(2) A
beneficiary shall not be entitled for the same period to an increase in benefit
under paragraph (1) in respect of more than one person.
28 Overlapping benefits, etc.
(1) Provision
may be made by Order –
(a) for adjusting benefit
payable to or in respect of any person, or the conditions for its receipt,
where –
(ai) any pension payable out
of the public funds of Jersey or the public funds of any other country or
territory is payable to or in respect of that person or that person’s wife,
husband or civil partner,
(aii) any payment has been made
under the Income
Support (Jersey) Law 2007, to or in respect of that person, or to or
in respect of a person who is a member of that person’s household for the
purposes of that Law,
(i) any allowance payable out of public funds
(including any other benefit under this Law whether of the same or a different
description) is payable to or in respect of that person or that person’s wife,
husband or civil partner, or
(ii) that person is
undergoing medical or other treatment as an in-patient in a hospital or similar
institution;
(b) for suspending payment of
benefit to a person during any period during which the person is undergoing
such medical or other treatment.[94]
(2) Where
by virtue of an Order made under paragraph (1) benefit payable to or in
respect of any person is adjusted, or the payment of any benefit is suspended,
by reason of the fact that the person is undergoing medical or other treatment
as an in-patient in a hospital or similar institution and such treatment is
provided free of charge to that person, the Minister, in his or her discretion,
may pay out of the Social Security Fund to the authority at whose expense the
treatment is provided the amount of the adjustment or the benefit, as the case
may be.
(3) Where
but for any Order made by virtue of paragraph (1)(a), 2 persons would both
be entitled to an increase of benefit in respect of a third person, provision
may be made by Order as to their priority.
(4) In
this Article, the expression “hospital or similar institution” includes any
institution in which poor persons are lodged and maintained at the cost of a
public or parochial authority.
29 Supplementary provisions
as to benefit
(1) Provision
may be made by Order –
(a) for prescribing the time
and manner in which claims to benefit may be made and the evidence and
information to be supplied in support thereof;
(b) for prescribing the time
and the manner of payment of benefit;
(c) for disqualifying a person
for receiving any benefit or suspending payment thereof during prescribed
periods of absence from Jersey or imprisonment or detention in legal custody;
(d) for prescribing the
circumstances in which a person is or is not to be deemed for the purposes of
this Law to be caring for another person;
(e) for any other matters
incidental to claims for and payment of benefit.[95]
(2) Subject
to the provisions of this Law, benefit shall not be capable of being assigned,
charged or attached, nor shall it pass to any other person by operation of law,
nor shall any claim be set off against the same, except in such cases and
subject to such conditions as may be prescribed.
PART 4
FINANCE, ADMINISTRATION AND LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
30 Social Security Fund
(1) The
Insular Insurance Fund established in pursuance of the Law of 1950 shall
be renamed the Social Security Fund and shall be maintained under the control
and management of the Minister.
(2) Subject
to paragraph (3A), there shall be paid into the Social Security Fund all
contributions payable under this Law after deduction therefrom of the
appropriate Health Insurance Fund Allocation and appropriate Long-Term Care
Fund Allocation, together with monies provided by the States, the proceeds of
all charges imposed under this Law and any amount recovered by virtue of Article 26I(1);
and there shall be paid out of the Fund all claims for benefit, and all
expenses, including salaries, equipment and the provision of accommodation,
incurred by the Minister in carrying this Law into effect.[96]
(3) Subject to paragraph (3A), the appropriate Health Insurance Fund Allocation, which shall be paid
into the Health Insurance Fund, shall be the aggregate of the amounts expressed
in Schedules 1A and 1B to be allocated to that Fund.[97]
(3A) Where
the Class 1 or Class 2 contributions paid in respect of a person are
less than such contributions as are due in respect of the person, the amount to
be paid into the Health Insurance Fund and the balance to be paid into the
Social Security Fund shall be reduced proportionally.[98]
(3B) The
appropriate Long-Term Care Fund Allocation, which shall be paid into the
Long-Term Care Fund, shall be the aggregate of –
(a) the LTC contributions
determined in accordance with Schedule 1C; and
(b) LTC surcharges determined
in accordance with paragraph 4A of Schedule 1D,
and collected in
accordance with Schedule 1D and the 1961 Law.[99]
(4) Annual
accounts shall be prepared in accordance with the accounting standards referred to
in the Public Finances Manual issued under the Public Finances (Jersey)
Law 2019.[100]
(5) Any
monies forming part of the Social Security Fund may, from time to time, be paid
over to –
(a) the Treasurer of the States; or
(b) an investment manager,
and may, by either of
them, be invested in accordance with such directions as may be given by the
Minister for Treasury and Resources.
(5A) The
Minister for Treasury and Resources may, after consultation with the Minister,
appoint one or more investment managers to whom money may be paid over pursuant
to paragraph (5) and may by Order make provision in relation to the
appointment of such managers.
(5B) An
Order made under paragraph (5A) shall include provisions –
(a) to ensure –
(i) the appointment of a suitable person or
persons, and
(ii) that regard is paid to
the need for diversification of investment of the assets of the fund;
(b) relating to the –
(i) suitability of investments which the
manager proposes to make,
(ii) retention of control by
the Minister for Treasury and Resources over the investments and over the
application of the assets of the fund, and
(iii) terms and conditions of
appointment of investment managers including the further delegation by such an
investment manager of the powers of management and investment given by such
appointment.
(5C) The
Minister for Treasury and Resources, in giving any directions as to the
application and investment or reinvestment of the monies of the Social Security
Fund paid over pursuant to paragraph (5), shall have regard to the –
(a) need for diversification
of investment of fund monies;
(b) suitability of
investments of any description which are proposed to be made; and
(c) obtaining, at reasonable
intervals, of proper advice.
(5D) In
this Article –
(a) “investment manager” means a person or persons reasonably
believed by the Minister to be suitably qualified by ability in and practical
experience of financial matters to make investment decisions on his or her
behalf;
(b) the reference in paragraph (5C)(c) to “proper advice” is a
reference to the advice of a person or persons reasonably believed by the
Minister for Treasury and Resources to be qualified by the
person’s ability
in and practical experience of financial matters to give such advice.
(6) The
Minister for Treasury and Resources may borrow money under the guarantee of the
annual income of the States in order to obtain currency, other than sterling,
required for any purpose connected with the investment of the Social Security
Fund.
(7) The
Minister for Treasury and Resources shall, on matters relating to investment,
provide full information to, and regularly consult with, the Minister and,
where such consultation does not end in agreement, the disagreement shall be referred
to the Council of Ministers for resolution.
(8) There
shall be presented to the States annually by the Minister an account of the
securities in which monies forming part of the Social Security Fund are for the
time being invested.
(9) [101]
31 Social Security (Reserve)
Fund
(1) The
Insular Insurance (Reserve) Fund established in pursuance of the Law
of 1950 shall be renamed the Social Security (Reserve) Fund and shall be
under the control and management of the Minister, and such assets as the
Minister may determine may be transferred from the Social Security Fund into
the Social Security (Reserve) Fund which shall be maintained as a reserve for
the Social Security Fund.
(2) Article 30(4),
(5), (5A), (5B), (5C), (5D), (6), (7), (8) and (9) shall apply to the Social
Security (Reserve) Fund as they apply to the Social Security Fund.
(3) Any
sums determined by the Minister to be income of the Social Security (Reserve)
Fund shall be paid into the Social Security Fund.
(4) Subject
to the foregoing provisions of this Article and any other provision of this Law
expressly directing payments to be made out of the Social Security (Reserve)
Fund, a payment out of that Fund shall not be made otherwise than under the
authority of a resolution of the States and shall be made subject to such
conditions as to repayment or otherwise as may be specified in the resolution.
32 Actuarial reports
(1) As from the end of the period of 3 years
from the appointed day, or such shorter period as the then Social Security
Committee directed, and, after that, in the year that
is immediately before a year in which an election is to be held under Article 6(1)
of the States of
Jersey Law 2005, and in such other year as the Minister may direct, an
actuary shall review the operation of this Law.[102]
(2) The actuary shall be appointed by the Minister.
(3) After
completing the review, the actuary shall report to the Minister on the
financial condition of the Social Security Fund and the adequacy or otherwise
of the contributions payable under this Law to support the benefits payable
thereunder having regard to its liabilities under this Law.
(4) A
copy of every report under this Article shall be laid before the States as soon
as may be after it is made.
33 Determination of claims
and questions[103]
(1) Subject
to this Law, provision shall be made by Order –
(a) for the determination of
any question arising under or in connection with this Law, including any claim
for benefit, by one or more officers appointed by the Minister, to be known as
determining officers; and
(b) if a person is
dissatisfied with any determination of a determining officer under this Law,
for the matter to be redetermined by a second determining officer.[104]
(2) Paragraph (1)
shall not apply to the determination by a medical board of any question for
which provision is made by Articles 34A to 34D.[105]
(3) Orders
under paragraph (1) shall provide for –
(a) appeals to the Tribunal
from any determination of a determining officer;
(b) the reference to the
Inferior Number of the Royal Court for decision of any question of law arising
in connection with the determination of a question by a determining officer or
of an appeal by the Tribunal;
(c) appeals to the Inferior
Number of the Royal Court from a decision of the Tribunal on any question of
law.[106]
(4) However,
the Tribunal shall not have jurisdiction unless a second determining officer
has first reconsidered the matter in accordance with an Order made under
paragraph (1)(b).[107]
(5) No
Order under this Article shall provide for appeals to lie from a decision of a
determining officer on questions –
(a) whether the contribution
conditions for any benefit are satisfied, or otherwise relating to an insured
person’s contributions;
(b) as to entitlement to a
death grant; or
(c) as to which of the 2 or
more persons satisfying the conditions for an increase of benefit, whether of
the same or of a different description, shall be entitled to the increase where
by virtue of some provisions of this Law not more than one of them is entitled
to the increase.[108]
(6) The
decision of the Inferior Number of the Royal Court on any reference or appeal
arising in connection with this Law shall be final and without further appeal,
but this is without prejudice to the right of the Inferior Number of the Royal
Court to refer the question at issue to the Superior Number of the Royal Court.
(7) Subject
to this Article, any Order under this Article may, in relation to any consideration
of a matter by a determining officer or the Tribunal in accordance with the
Order, include provision –
(a) as to the procedure which
is to be followed, the form which is to be used for any document, the evidence
which is to be required and the circumstances in which any official record or
certificate is to be sufficient or conclusive evidence;
(b) as to the time to be
allowed for making any claim or appeal, for raising any question with a view to
the review of any decision or for producing any evidence;
(c) for summoning persons to
attend and give evidence or produce documents and for authorizing the
administration of oaths to witnesses; or
(d) for the representation of
one person, at any hearing of a case, by another person, whether or not that
other person has professional qualifications.[109]
(8) Where,
in any proceedings for an offence under this Law, involving any question as to
the payment of contributions under this Law or for the recovery of any sums due
to the Social Security Fund, any question arises that is required by an Order
under this Article to be determined in accordance with the Order, provision may
be made by Order –
(a) that the decision
relating to that question shall be conclusive for the purpose of those
proceedings;
(b) for obtaining such a
decision when it has not been given; and
(c) for adjourning the
proceedings until such a decision has been given.
(9) In
this Article, “Tribunal” means –
(a) in the case of any appeal
from any determination of a determining officer as to whether, for the purposes
of Article 18A(1)(a), a carer is regularly and substantially engaged in
caring for a cared for person or whether a cared for person meets the criteria
described in Article 18A(3)(a) – the Medical Appeal Tribunal
constituted under Article 9(2)(a) of the Income Support (Jersey)
Law 2007; and
(b) in the case of any other
appeal from any determination of a determining officer – the Social
Security Tribunal constituted under Article 33A.[110]
33A Social Security Tribunal[111]
(1) The
Minister shall by Order prescribe the constitution of the Social Security
Tribunal.
(2) The
Minister may pay to any member of the Social Security Tribunal who exercises
any functions under this Law, such remuneration and expenses as the Minister
may determine.
34 Social Security Medical
Appeals Tribunal[112]
(1) The
Minister shall, by Order, prescribe the constitution of the Social Security
Medical Appeals Tribunal.
(2) Subject
to the provisions of this Law, the Minister may, by Order, prescribe procedures
to be followed by the Social Security Medical Appeals Tribunal in the discharge
of its functions under this Law.
(3) Orders
under this Article shall provide for –
(a) the reference to the
Inferior Number of the Royal Court for decision of any question of law arising
in connection with the determination of an appeal to the Social Security
Medical Appeals Tribunal; and
(b) appeals to the Inferior
Number of the Royal Court from a decision of that Tribunal on any question of
law,
and a decision of the
Inferior Number of the Royal Court on any such reference or appeal shall be
final and without further appeal, without prejudice to the right of the
Inferior Number of the Royal Court to refer the question at issue to the
Superior Number of the Royal Court.[113]
34AA Medical boards[114]
(1) The
Minister shall appoint medical boards, each consisting of one or 2 medical
practitioners.
(2) Subject
to the provisions of this Law –
(a) the Minister may, by
Order, prescribe the procedures to be followed by a medical board in the
discharge of its functions under this Law; and
(b) where –
(i) a person claiming long term incapacity
allowance is dissatisfied with any determination of a question by a medical
board, or
(ii) the Minister considers
that a question decided by a medical board should be reconsidered,
the question shall be
reconsidered by a second medical board, and further provision as to the
procedures to be followed in relation to such reconsideration may be made by
Orders under this Article.[115]
(3) For
the purposes of this Article and Articles 34B and 34C, a ‘second medical
board’ means a board consisting of one or 2 medical practitioners who are
not the same medical practitioners as those appointed to the medical board
whose determination or (as the case may be) decision is to be reconsidered.[116]
34A Determination of questions
relating to loss of faculty[117]
(1) Where
a person claims long term incapacity allowance, any question as to a matter listed
in paragraph (2) shall be referred by the Minister to a medical board for
determination.[118]
(2) The
matters mentioned in paragraph (1) are –
(a) whether a relevant
disease or injury has resulted in a loss of faculty;
(b) whether a loss of faculty
is likely to be permanent;
(c) the degree at which
incapacitation resulting from a loss of faculty is to be assessed; and
(d) the period to be taken
into account in the assessment of the degree of incapacitation.[119]
(3) Where
the medical board has assessed the degree of incapacitation in accordance with paragraph (2)(c),
before the end of the period to be taken into account as determined by the
medical board under paragraph (2)(d), the Minister shall refer the case
again to a medical board, for further determination of the matters listed in paragraph (2).[120]
34B Appeals from determinations
by medical boards[121]
(1) Subject
to paragraph (3), a claimant shall have a right of appeal to the Social
Security Medical Appeals Tribunal against a decision of a second medical board
under this Law.[122]
(2) An
appeal shall be made in such manner and brought within such time as may be
prescribed.
(3) For
the avoidance of doubt, the Social Security Medical Appeals Tribunal shall not
have jurisdiction to hear an appeal from a decision of a medical board unless a
second medical board has first reconsidered the matter in accordance with an
Order made under Article 34AA(2)(b).[123]
(4) On
hearing an appeal, the Social Security Medical Appeals Tribunal may confirm,
reverse or vary the decision against which the appeal is brought.[124]
34C References by Minister
to Social Security Medical Appeals Tribunal[125]
(1) Where
the Minister considers that a decision of a second medical board ought to be
considered by the Social Security Medical Appeals Tribunal, the Minister may
refer the case to that Tribunal for its consideration.
(2) A
reference by the Minister under paragraph (1) shall be made within 14 days
of the decision in question.
(3) On
considering a case referred by the Minister, the Social Security Medical
Appeals Tribunal may confirm, reverse or vary the decision in question.
(4) The
Minister may by Order amend the period in paragraph (2).
34D Further reviews[126]
(1) Where
a determining officer is satisfied by fresh evidence that a decision of any
medical board or by the Social Security Medical Appeals Tribunal was given as a
result of non-disclosure or misrepresentation of a material fact (whether by
the claimant or another person, and whether fraudulently or innocently), the
determining officer shall refer the decision to a further medical board for
review.[127]
(2) Independently of any review under paragraph (1),
on referral by a determining officer following consideration as described
in paragraph (3), and subject to paragraph (4), a further medical
board may also review an assessment by any medical
board or by the Social Security Medical Appeals Tribunal on the ground that,
since the making of the assessment, there has been either –
(a) a substantial aggravation;
or
(b) a substantial
amelioration,
of the results of the
relevant disease or injury.[128]
(3) A
medical board shall not under paragraph (2) review an assessment unless a
determining officer has considered any fresh evidence and determined whether
any aggravation or (as the case may be) amelioration is so substantial as to
merit such review of the assessment.[129]
(4) A
medical board shall not under paragraph (2) review an assessment on any
application made within 3 months of the assessment.[130]
(5) [131]
(6) [132]
(7) [133]
(8) Subject
to the other provisions of this Article, a medical board may on a review deal
with a case in any manner in which it may deal with a case on an original
reference.[134]
(9) The
provisions of this Law shall apply to a decision on a review under this Article
as if it were an original decision.
34E Power to refer questions to
experts[135]
(1) Where
any question of special difficulty falls to be determined under any of Articles 33,
34A, 34B, 34C or 34D, the person or body responsible for such determination may
refer that question to one or more experts for examination and report.
(2) An
expert to whom a question is referred under paragraph (1) shall not
disclose any information coming to his or her knowledge as a result of such
referral to any person except –
(a) a person acting in
execution of this Law;
(b) as may be required for
any purpose approved by the Minister; or
(c) for the purposes or in
the course of any legal proceedings,
but Article 49 shall
not apply to the expert.
(3) In
this Article “expert” means a person appearing to the person or body
responsible for the determination to have knowledge or experience which would
be relevant in determining the question of special difficulty.
35 Powers of inspection
(1) Any
officer in an administration of the States for which the Minister is assigned
responsibility who is generally or specially authorized in writing by the
Minister in that behalf (in this Article referred to as an “inspector”) shall,
for the purposes of the execution of this Law, be entitled, subject to the
production by the officer if so required of evidence of the officer’s
authority, to do all or any of the following things, namely to –
(a) enter at all reasonable
times any premises or place liable to inspection under this Article;
(b) make such examination and
inquiry as may be necessary for ascertaining whether the provisions of this Law
are being or have been complied with in any such premises or place;
(c) examine, either alone or
in the presence of any other person, as the officer thinks fit, with respect to
any matters under this Law on which the officer may reasonably require
information, every person whom the officer finds in any such premises or place,
or whom the officer has reasonable cause to believe to be or to have been an
insured person, and to require every such person to be so examined;
(d) exercise such other
powers as may be necessary for carrying this Law into effect.
(2) The
occupier of any premises or place liable to inspection under this Article, and
any person who is or has been employing any person (and the servants and agents
of any such occupier or other person) and any person carrying on any agency or
other business for the introduction or supply to persons requiring them of
persons available to do work or perform services (and the servants or agents of
any person carrying on any such agency or other business), and any insured person,
shall furnish to an inspector all such information and produce for inspection
all such documents as the inspector may reasonably require for the purpose of
ascertaining whether contributions are or have been payable, or have been duly
paid, by or in respect of any person, or whether benefit is or was payable to
or in respect of any person.
(3) If
any person –
(a) wilfully delays or
obstructs an inspector in the exercise of any power under this Article; or
(b) refuses or neglects to
answer any question or to furnish any information or to produce any document
when required to do so under this Article,
he or she shall be liable
to a fine not exceeding level 2 on the standard scale in the case of a first
offence under this paragraph and, where a person is convicted of an offence
under sub-paragraph (b) and the refusal or neglect is continued by him or
her after conviction, he or she shall be guilty of a further offence and be
liable on conviction to a fine not exceeding level 1 on the standard scale for
each day on which it so continued:
Provided that no person
shall be required under this Article to answer any questions or to give any
evidence tending to incriminate himself or herself.[136]
(4) The
premises and places liable to inspection under this Article are any premises or
places where an inspector has reasonable grounds for supposing that –
(a) any persons are employed;
(b) there is being carried on
any agency or other business for the introduction or supply to persons
requiring them of persons available to do work or perform services,
except that they do not
include any private dwelling house not used by or by permission of the occupier
for the purposes of a trade or business.
36 General provisions as to
offences and penalties
(1) Paragraph (1A)
applies where an employer is required to furnish prescribed information to the
Minister before a prescribed date to enable the Minister to calculate any
amount of Class 1 contribution payable by the employer.[137]
(1A) If
the employer fails to furnish the information before the prescribed date the
employer is liable to pay an additional contribution equal to 5% of the amount
of the Class 1 contribution unless the employer satisfies the Minister
that it was not reasonably possible to furnish the required information before
the prescribed date.[138]
(1B) If
the employer fails to pay any amount of Class 1 contribution, including
any additional contribution payable under paragraph (1A), before the date
prescribed for the payment of the Class 1 contribution the employer shall
be liable to pay an additional 1% of the amount unpaid and shall also be liable
to pay interest at the of rate of 1% of any amount unpaid for each month it
remains unpaid.[139]
(1C) A
rate of interest mentioned in paragraph (1A) or (1B) may be amended by the
States by Regulations.[140]
(2) An
employer or insured person who fails to pay a contribution that he or she is
liable to pay under this Law within the time prescribed for payment of the
contribution shall be guilty of an offence and liable to a fine not exceeding
level 3 on the standard scale.[141]
(3) A
person who, for the purpose of obtaining a benefit or other payment under this
Law, whether for himself, herself or some other person, or for any other
purpose connected with this Law –
(a) knowingly makes a false
statement or false representation; or
(b) produces or furnishes, or
causes or knowingly allows to be produced or furnished, a document or any
information that the person knows to be false in a material particular,
shall be guilty of an
offence and liable to imprisonment for a term not exceeding 7 years or to a
fine, or both.[142]
(4) Provision
may be made by Order for the recovery of monetary penalties in respect of any
offence under this Law, being a contravention of or failure to comply with any
provisions of the Order, so, however, that such penalties shall not exceed
level 3 on the standard scale for each offence or, where the offence consists
of continuing any such contravention or failure after conviction thereof, level
3 on the standard scale together with a further level 1 on the standard scale
for each day on which it is so continued.[143]
(5) Where
an offence under this Law which has been committed by a body corporate is
proved to have been committed with the consent or connivance of, or to be
attributable to any negligence on the part of, any director, manager, secretary
or other officer of the body corporate, or any person who was purporting to act
in any such capacity, he or she as well as the body corporate shall be deemed
to be guilty of that offence and shall be liable to be proceeded against and
punished accordingly.
38 Civil proceedings to
recover sums due to Social Security Fund
Proceedings for the
recovery of sums due to the Social Security Fund may be instituted by the
Treasurer of the States, either in term or in vacation, and, notwithstanding
any enactment or rule of Law to the contrary, any such proceedings may be
brought at any time within 10 years from the time when the matter complained of
arose.[144]
39 Recovery of sums due to
Social Security Fund by deductions from earnings
(1) Where
judgment has been obtained for the payment of any sum due to the Social
Security Fund by any individual (in this Article referred to as the “judgment
debtor”) then, notwithstanding any enactment or rule of law to the contrary and
without prejudice to any other means of recovery, the sum payable under the
judgment together with the recoverable costs (in this Article referred to as the
“judgment debt”) may be recovered in accordance with the provisions of this Article.
(2) Where
it is desired to recover any judgment debt under this Article –
(a) the Minister may serve
notice on the employer for the time being of the judgment debtor requiring the
employer to furnish the Minister, within such time (not being less than
7 days) as may be specified in the notice with a certificate of the amount
earned by the judgment debtor in the employ of the employer during such past
period or periods as may be so specified; and
(b) whether or not such a
certificate as aforesaid has been required to be furnished, the Minister may
serve notice on the employer for the time being of the judgment debtor
requiring the employer to make such deductions from the earnings of the
judgment debtor as may, having regard to all the circumstances of the case,
appear to the Minister to be reasonable and to pay the amounts so deducted to
the Minister at such times as may be specified in the notice, and the amount so
paid shall be applied towards the satisfaction of the judgment debt:
Provided that where the
judgement debt has been ordered to be paid by instalments, the Minister shall
not require such deductions to be made as would at any date reduce the judgment
debt by a greater amount than that by which it would have been reduced had the
instalments been paid.
(3) Any
employer who refuses or without lawful excuse fails to furnish a certificate
which under paragraph (2)(a) the employer is required to furnish within
such time as may be so required, or who furnishes a certificate which is false
in a material particular, shall be liable to a fine not exceeding level 2 on
the standard scale.[145]
(4) Any
notice under paragraph (2)(b) may at any time be varied by a subsequent
notice under that sub-paragraph.
(5) A
copy of every notice served under paragraphs (2)(b) or (4) shall be served
also on the judgment debtor.
(6) Where
any employer fails to deduct any amount which the employer is required by
virtue of paragraph (2)(b) to deduct, or to pay to the Minister any amount
so deducted, the amount may be recovered from the employer as a debt due to the
Social Security Fund.
(7) Service
of any notice under this Article may be effected by sending it by registered
post to the person on whom it is to be served at his or her usual or last known
place of abode or his or her principal place of business or, in the case of a
company, at its registered office.
40 Benefit and assessment of
damages
Where an insured person
suffers injury in circumstances creating a legal liability in any person to pay
damages to the insured person, the Court shall not, in assessing such damages,
take into account any benefit which the insured person is entitled to claim as
a result of such injury.
41 Recovery in bankruptcy, etc.
(1) Where
the Royal Court has granted –
(a) an application by any person
to place his or her property under the control of the Court (de remettre ses biens entre les mains de
la Justice); or
(b) an application for the
holding of a bénéfice
d’inventaire on the estate of any deceased person,
the autorisés or the Viscount, as the case may be,
shall pay out of the property of such person or the estate of such deceased person
any amount due to the Social Security Fund by such person or such deceased person
at the time of the granting of the application.
(2) In
the event of any dégrèvement, réalisation, désastre, bankruptcy or composition with creditors,
any amount due to the Social Security Fund shall rank for payment pari passu with other privileged debts and in
priority to all other debts.
42 [146]
PART 5
MISCELLANEOUS AND GENERAL
43 Crown servants and
members of Armed Forces
(1) This
Law shall apply to persons employed by or under the Crown, subject to any
special provision made by virtue of this Article, in like manner as if the
employer were a private person, with such modifications as the Minister may by
Order make thereto for the purpose of adapting the provisions thereof to the
case of such persons.
(2) Subject
to any prescribed exceptions, any person who is serving as a member of any of Her
Majesty’s Forces or of any prescribed organisation in which persons serve under
the control of the Defence Council shall be deemed not to be an insured person
whilst the person is serving as aforesaid.
44 Mariners and airmen
Without prejudice to the
generality of any other power to make Orders, the Minister may make Orders
modifying in such manner as the Minister thinks proper the provisions of this Law
in their application in relation to persons who are or have been employed on a
ship, vessel, hovercraft or aircraft and any Order may in particular provide
for –
(a) this
Law to apply to such persons notwithstanding that it would not otherwise apply;
(b) excepting
such persons from the application of this Law where they neither are domiciled
nor have a place of residence in Jersey;
(c) requiring
the payment of secondary Class 1 contributions in respect of such persons
whether or not they are insured persons;
(d) the
taking of evidence for the purpose of any claim to benefit, in a country or
territory outside Jersey by a British Consular Officer or such other person as
may be prescribed;
(e) enabling
persons who are or have been so employed to authorize the payment of the whole
or any part of any benefit to which they are or may become entitled to such of
their dependants as may be prescribed.
45 [147]
46 Insured persons outside
Jersey
(1) Without
prejudice to the generality of any other power to make Orders, the Minister may
make Orders modifying in such manner, subject to the provisions of paragraph (2),
as the Minister thinks proper, the provisions of this Law in their application
in relation to persons who are or have been outside Jersey while insured under
this Law.
(2) Orders
under this Article shall provide that, where an insured person is throughout
any contribution month outside Jersey and is not in that month an employed person,
he or she shall not be liable to pay any contribution as an insured person for
that month.
(3) Without
prejudice to the generality of the provisions of paragraph (1), Orders
thereunder may make provision for entitling a person to pay a Class 2
contribution for any month for which by virtue of paragraph (2) he or she
is not liable to pay a contribution as an insured person.
47 Class 2 insured persons nearing pensionable age[148]
(1) Provision
may be made by Order for excepting Class 2 insured persons who so elect, and
who have attained the Class 2 contribution exception age specified in the
person’s case in Schedule 1AA and satisfy such other conditions as may be
prescribed, from liability to pay Class 2 contributions otherwise payable under
this Law.[149]
(2) A
person who has been excepted from liability to pay Class 2 contributions by
virtue of paragraph (1) and who subsequently ceases to be so excepted
shall not be entitled to pay Class 2 contributions in respect of any period
during which he or she was so excepted.[150]
48 Reciprocal agreements
with other countries
(1) For
the purpose of giving effect to any agreement with the government of the United
Kingdom or of any part of Her Majesty’s dominions, or the government of any
other country, (including any agreement between the government of the United
Kingdom and the government of any part of Her Majesty’s dominions or of any
foreign country, which has been extended or applies to Jersey), providing for
reciprocity in matters relating to payments in respect of incapacity, accident,
confinement of women, widowhood, old age or death, the States may, by Act, provide for this Law to
be read as modified or adapted, in its application to cases affected by the
agreement, to the extent required by the agreement.[151]
(2) Where the States have made an Act under
paragraph (1), this Law shall be read as modified so as to include
provision for –
(a) securing that acts,
omissions and events having any effect for the purpose of the law of the
country in respect of which the agreement is made shall have a corresponding
effect for the purposes of this Law;
(b) determining in cases
where rights accrue both under this Law and under the law of the said country,
which of those rights shall be available to the person concerned;
(c) making any provisions as
to administration and enforcement contained in this Law, or in any enactment
thereunder, applicable also for the purposes of the law of the said country;
(d) making any necessary
financial adjustments by payments into or out of the Social Security Fund.[152]
49 Oath of Office[153]
The chief officer
appointed to administer this Law (the “Controller”) shall, before he or she
begins to act in execution of this Law, take oath of office before the Royal
Court in the form set out in Schedule 3, but notwithstanding the oath of
office the Controller may disclose such information as may be required for any
purpose approved by the Minister.
50 Power to amend Law by
Regulations[154]
(1) The States may by Regulations amend in this
Law –
(a) in respect of insured
persons –
(i) who is an insured person for the purposes
of this Law,
(ii) the classification of
insured persons for the purposes of this Law,
(iii) the liability of insured
persons to pay contributions,
(iv) the amounts of the
contributions payable by insured persons,
(v) the circumstances in which an insured
person is entitled to a contribution credit, rules for calculation of
contribution credits and circumstances in which an insured person is or may be
entitled to a backdated contribution credit;
(b) in respect of employers
of insured persons –
(i) who is an employer of an insured person
for the purposes of this Law,
(ii) the liability of
employers of insured persons to pay contributions in respect of those persons,
(iii) the amounts of the
contributions payable by employers of insured persons in respect of those
persons;
(c) in respect of the
collection of contributions, the manner in which, when and by whom
contributions are to be paid;
(d) in respect of
benefits –
(i) the descriptions of benefit,
(ii) who is entitled to a
benefit of any description,
(iii) the conditions for a
person’s entitlement to a benefit of any description,
(iv) the period or periods for
which a person is entitled to a benefit of any description,
(v) the rate or amount of any benefit
(including a standard rate of benefit),
(vi) the circumstances in
which and the extent to which any benefit shall or may be backdated;
(e) in respect of the Social
Security Fund –
(i) the rules for calculation of amounts to be
allocated to the Health Insurance Fund or the
Long-Term Care Fund before contributions are paid into
the Social Security Fund,
(ii) the purposes for which
money shall be paid out of the Social Security Fund and, where appropriate, how
the amount to be paid out is to be determined;
(f) any provision for the
payment of money into the Social Security Fund by the States –
(i) where the States is or is to be required
to make payments, as to how the amounts are to be determined, the periods to
which they are to relate and when they are to be paid, or
(ii) so as to remove any
obligation for the States to make payments into the Fund.[155]
(2) Without prejudice to the generality of
paragraph (1)(a)(iii) and (iv) Regulations may –
(a) amend the definition
‘earnings’ in Article 1;
(b) add a definition ‘income’
in Article 1;
(c) amend this Law to provide
that an insured person’s contributions are calculated by reference to the
person’s income; and
(d) amend this Law to provide
for the determination of the amount of an individual’s earnings or income for a
specified period.
(3) The States may by Regulations amend this
Law so as to provide for the aggregation of contributions of different classes.
(3A) The States may by Regulations amend in, or
add to, this Law provision for the imposition of a surcharge where
contributions of any specified class are not paid, whether by the insured
person or any other person, by the date required by or under this Law.[156]
(4) Regulations made under this Article may
also, for the purposes of supplementing any amendment made pursuant to
paragraphs (1) to (3) –
(a) amend in this Law any
power to make an Order; and
(b) amend this Law to provide
that any further matter shall or may be made by Order.
(5) Regulations made under this Article may
amend any other enactment consequentially upon any amendment of this Law made
pursuant to paragraphs (1) to (3).
(5A) Regulations made under this Article may amend
Article 49B of, and Schedule 1A to, the 1961 Law.[157]
(6) Regulations made under this Article shall
not amend this Article or Article 51.
(7) Draft Regulations to be made by the States
under this Article may only be lodged by the Minister.
51 General provisions as to
Acts, Regulations and Orders
(1) Except
in so far as this Law otherwise provides, any power conferred thereby to make
any Act or Regulations or Order may be exercised –
(a) either in relation to all
cases to which the power extends, or in relation to all those cases subject to
specified exceptions, or in relation to any specified cases or classes of case;
and
(b) so as to make, as
respects the cases in relation to which it is exercised –
(i) the full provision to which the power
extends or any less provision (whether by way of exception or otherwise),
(ii) the same provision for
all cases in relation to which the power is exercised or different provision
for different cases or classes of case, or different provision as respects the
same case or class of case for different purposes of this Law,
(iii) any such provision either
unconditionally or subject to any specified condition.
(2) Without
prejudice to any specific provision of this Law, any Act, Regulations or Order
under this Law may contain such transitional, incidental or supplementary
provisions as appear to the States or, as the case may be, the Minister making
the Order, to be expedient for the purposes of the Act, Regulations or Order.[158]
(3) The
Subordinate
Legislation (Jersey) Law 1960 shall apply to Orders made under this Law.
54 Provisions as to
commencement
(1) In
this Law, the expression the “appointed day” means, subject to the following
provisions of this Article, such day as the States may by Act appoint and
different days may be appointed for different purposes of this Law or for the
same purpose in relation to different cases or classes of case.[159]
(2) Any
Act under paragraph (1) may, if the day thereby appointed is appointed for
some only of the purposes of this Law or in relation only to some cases or
classes of case, contain such incidental or supplementary provisions as appear
to the States to be necessary or expedient as respects the period when this Law
is to have a partial operation only or as respects the transition from that
period to the period when this Law is in full operation.
(3) Without
prejudice to the generality of the provisions of paragraph (2), the
provisions which may be made thereunder include, in particular, provision for
modifying and supplementing in relation to the period to which the Act is to
apply, the provisions of this Law, and where the repeal of the Law of 1950
has not yet taken effect, the provisions of that Law.
54A Transitional[160]
(1) Notwithstanding
the amendment of this Law by Articles 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13,
14,16 and 17 of the Social Security (Amendment No. 14) (Jersey)
Law 2000 (in this Article called the “2000 Law”) , if
any person was entitled immediately before the commencement of the 2000 Law
to any description of benefit under this Law –
(a) the person’s entitlement
to that benefit shall from the commencement of the 2000 Law be determined
as if that Law had not been passed; and
(b) the person shall not be
entitled, in respect of the circumstances in which he or she became entitled to
that benefit, to receive benefit under this Law as amended by those Articles of
the 2000 Law.
(2) Notwithstanding
its repeal by Article 15 of the 2000 Law, Article 45 of this Law[161] shall continue to apply to every woman who was married before its
repeal.
54B Transitional arrangements:
replacement of invalid care allowance by home carer’s allowance[162]
(1) This
paragraph applies where –
(a) immediately before
commencement, a person (the “first person”) was, under the 1978 Law, entitled
to invalid care allowance in respect of the care of a severely disabled person
(the “second person”); and
(b) the first person had
claimed such allowance before commencement.
(2) In
a case to which paragraph (1) applies, upon commencement –
(a) the first person shall,
for the purposes of Article 18A(1)(a), be taken to be regularly and
substantially engaged in caring for the second person;
(b) the first person shall be
taken to satisfy any residency requirement prescribed under Article 18A(2)(a);
(c) the first person shall be
taken to satisfy the requirement in Article 18A(2)(b);
(d) the second person shall
be taken to satisfy any residency requirement prescribed under Article 18A(3)(b).
(3) Paragraph (2)(a)
shall cease to have effect upon the completion of the first review carried out,
following commencement, in the prescribed circumstances, of the first person’s
entitlement to home carer’s allowance.
(4) The
references in Article 18A(4)(a) and (b) to a person having been entitled
to and claimed home carer’s allowance include references to a person having
been entitled to and claimed invalid care allowance.
(5) Notwithstanding
the provisions of any Order made under Article 28, where a person was,
immediately before commencement, in receipt of invalid care allowance and
survivor’s benefit, an adjustment shall not be made, in the person’s case,
between home carer’s allowance and survivor’s benefit.
(6) In
this Article –
“1978 Law” means the Invalid
Care Allowance (Jersey) Law 1978;
“commencement” means the
day Part 2 of the Social Security (Amendment of Law No. 4) (Jersey)
Regulations 2012 came into force;
“invalid care allowance”
means the allowance that, before commencement, was payable under the
1978 Law.
54C Transitional arrangements:
survivor’s benefit[163]
(1) Article 24(1)(b)(iv)
and (5) shall not apply in the case of a person who –
(a) immediately before
commencement, was entitled to survivor’s benefit; or
(b) before commencement, has
attained the age of 55.
(2) In
this Article, “commencement” means the day Part 5 of the Social Security
(Amendment of Law No. 4) (Jersey) Regulations 2012 came into force.
54D Transitional provision for
LTC contributions in 2015[164]
(1) Any
notice issued by the Comptroller in 2015 in respect of a person’s LTC
contribution for that year shall be taken to be a notice of the estimate of
that amount served and calculated under paragraphs 2 and 2A of Schedule 1D
as amended by the Social Security (Amendment of Law No. 10) (Jersey)
Regulations 2015.
(2) In
paragraph (1) “Comptroller” has the same meaning as in Schedule 1D.
54E Transitional provision for
payment of LTC instalment in 2020[165]
(1) A
person must pay an instalment of their LTC contribution for the 2020 year
of assessment if –
(a) the person is required to
pay an instalment of income tax under paragraph 25 of Schedule 5 to
the 1961 Law; and
(b) the person is an insured
person.
(2) The
instalment is due and payable on 31st May 2021.
(3) If,
at 31st May 2021, an income tax assessment has not been made for the
person for the 2020 year of assessment, the amount of the person’s
instalment is calculated as follows –
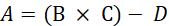
Where –
A is the amount of the instalment;
B is 0.5 if the person’s income for the year before the
year of assessment did not include any earnings, and is 0.4 in any other
case;
C is the person’s estimated LTC contribution for the 2020
year of assessment (determined in accordance with paragraph 2A of
Schedule 1D); and
D is the amount of LTC contribution already paid for
the 2020 year of assessment (not including an amount deducted under
Article 41B or 41E of the 1961 Law).
(4) If,
at 31st May 2021, an income tax assessment has been made for a person for
the 2020 year of assessment, the amount of the person’s instalment is the
lower of –
(a) the person’s remaining
LTC contribution liability for the 2020 year of assessment; and
(b) the amount calculated
using the formula in paragraph (3).
(5) If
a person’s instalment of income tax under paragraph 25 of Schedule 5
of the 1961 Law is waived or reduced under Article 41AA of that Law,
the person’s instalment of LTC contribution is correspondingly waived or
reduced and the Comptroller must repay any amount determined to have been
overpaid.
(6) In
this Article, unless the context requires otherwise, terms defined in the
1961 Law but not in this Law have the meaning given in the 1961 Law.
55 Citation
This Law may be cited as
the Social Security (Jersey) Law 1974.
SCHEDULE 1AA[166]
(Articles 1A, 8A(6),
8A(7), 25(1A)(a) and 47(1))
pensionable age
1 Pensionable age
A person’s pensionable age is
the age specified in column 2 of the table, below, opposite the age
category specified in column 1 of the table in which the person’s date of
birth falls.
2 Contribution years under Article 8A
A person’s contribution
years, for the purposes of Article 8A(6) and (7), is the period specified
in column 3 of the table, below, opposite the age category specified in
column 1 of the table in which the person’s date of birth falls.
3 Election to take reduced old age pension under Article 25
A person’s reduced pension
age, for the purposes of Article 25(1A)(a), is the age specified in
column 4 of the table, below, opposite the age category specified in
column 1 of the table in which the person’s date of birth falls.
4 Election in respect of Class 2 contributions under
Article 47
A person’s Class 2 contribution
exception age, for the purposes of Article 47(1), is the age specified in
column 5 of the table, below, opposite the age category specified in
column 1 of the table in which the person’s date of birth falls.
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
|
Age
categories
|
Pensionable
age
|
Contribution
years for the purposes of Article 8A
|
Reduced
pension age for the purposes of Article 25(1A)
|
Class
2 contribution exception age for the purposes of Article 47(1)
|
|
Person
born before 1st January 1955
|
65
|
45
|
63
|
60
|
|
Person
born on or after 1st January 1955 and before 1st November 1955
|
65 years and 2 months
|
45
|
63
|
60
|
Person born on or after 1st
November 1955 and before 1st September 1956
|
65 years and 4 months
|
45
|
63
|
60
|
|
Person
born on or after 1st September 1956 and before 1st July 1957
|
65 years and 6 months
|
45
|
63
|
60
|
|
Person
born on or after 1st July 1957 and before 1st May 1958
|
65 years and 8 months
|
45
|
63
|
60
|
|
Person
born on or after 1st May 1958 and before 1st March 1959
|
65 years and 10 months
|
45
|
63
|
60
|
|
Person
born on or after 1st March 1959 and before 1st January 1960
|
66 years
|
46
|
64
|
61
|
|
Person
born on or after 1st January 1960 and before 1st November 1960
|
66 years and 2 months
|
46
|
64
|
61
|
|
Person
born on or after 1st November 1960 and before 1st September 1961
|
66 years and 4 months
|
46
|
64
|
61
|
|
Person
born on or after 1st September 1961 and before 1st July 1962
|
66 years and 6 months
|
46
|
64
|
61
|
|
Person
born on or after 1st July 1962 and before 1st May 1963
|
66 years and 8 months
|
46
|
64
|
61
|
|
Person
born on or after 1st May 1963 and before 1st March 1964
|
66 years and 10 months
|
46
|
64
|
61
|
|
Person
born on or after 1st March 1964
|
67 years
|
47
|
65
|
62
|
SCHEDULE 1A[167]
(Articles 5(4), 9 and
30(3))
class 1 factors and
contribution rates
1 Class 1 – earnings
For the purposes of
determining the amount of Class 1 contributions payable in respect of a
Class 1 insured person, and subject to any Order made under Article 1(5)
or 11, the earnings of a Class 1 insured person include any sums payable
to the person (whether under a contract of service or any other office, employment
or arrangement whereby the person is rewarded for work done or services
rendered) by way of wages, salary, fees, bonuses, commission, overtime pay or
any other emolument including the value of any loan, perquisite or any other
benefit in kind.
2 Class 1 – monthly earnings limits
(1) For the purposes of this Law, subject to sub-paragraphs (2)
and (3) –
(a) the lower monthly
earnings limit for Class 1 contributions is £776;
(b) the standard monthly
earnings limit for Class 1 contributions is £3,686;
(c) the upper monthly
earnings limit for Class 1 contributions is £20,800.
(2) On
the 1st January in 2012 and every subsequent year, the limits in sub-paragraph (1)(a)
and (b) shall each be increased or decreased, as the case requires, by the percentage
figure equal to the percentage rise or fall in the Jersey Index of Earnings
during the 12 months ending on 30th June in the preceding year.
(3) On
the 1st January in 2021 and every subsequent year, the limit in
sub-paragraph (1)(c) shall be increased or decreased, as the case
requires, by the percentage figure equal to the percentage rise or fall in the
Jersey Index of Earnings during the 12 months ending on 30th June in the
preceding year.
3 Class 1 – monthly contributions
(1) The
amount of an employed person’s primary Class 1 contributions in respect of
the monthly earnings of an employment is the aggregate of the following
amounts –
(a) 0.8% of the person’s
earnings that do not exceed the standard monthly earnings limit, which amount
shall be allocated to the Health Insurance Fund; and
(b) 5.2% of the person’s
earnings that do not exceed the standard monthly earnings limit.
(2) The
amount of an employer’s secondary Class 1 contributions in respect of the
monthly earnings of an employee is the aggregate of the following
amounts –
(a) 1.2% of the employee’s
earnings that do not exceed the standard monthly earnings limit, which amount
shall be allocated to the Health Insurance Fund;
(b) 5.3% of the employee’s
earnings that do not exceed the standard monthly earnings limit; and
(c) 2.5% of the employee’s
earnings that exceed the standard monthly earnings limit but do not exceed the
upper monthly earnings limit.
3A Class 1 – standard contribution
The standard contribution for
a month is, in the case of a Class 1 insured person, the sum of –
(a) the
maximum amount payable under paragraph 3(1)(b) for the month; and
(b) the
maximum amount payable under paragraph 3(2)(b) for the month.
4 Class 1 –
supplementation
(1) Where –
(a) contributions
have been paid in respect of a Class 1 insured person for a month; and
(b) the
sum of the social security contributions paid and credited in respect of the
Class 1 insured person for the month exceed the contribution threshold but
are less than the standard contribution,
the
social security contributions shall be supplemented for the month by an amount
sufficient to cause those contributions in respect of the person for the month
to equal the standard contribution.
(2) No
supplementation shall be awarded in respect of –
(a) secondary
Class 1 contributions alone; or
(b) social
security contributions paid and credited in respect of a person which exceed
the contribution threshold but are less than the standard contribution but
which would not have been less than the standard contribution had contribution
liability been discharged in full.
(3) For
the purposes of this paragraph –
(a) the contribution
threshold is the sum of –
(i) 5.2% of the lower monthly earnings limit,
and
(ii) 5.3% of the lower
monthly earnings limit;
(b) “social security
contributions” means so much of the contributions paid or credited in respect
of a Class 1 insured person as are to be paid into the Social Security
Fund.
SCHEDULE 1B[168]
(Articles 8(3), 9 and
30(3))
class 2 factors and
contribution rates
1 Class 2 – earnings
For the purposes of
determining the amount of Class 2 contributions payable in respect of a
Class 2 insured person, and subject to any Order made under Article 1(5)
or 11, the earnings of a Class 2 insured person include any sums payable
to the person (whether under a contract for services or any office or
arrangement whereby the person is rewarded for work done or services rendered)
by way of wages, salary, fees, bonuses, commission, overtime pay or any other
emolument including the value of any loan, perquisite or any other benefit in
kind.
2 Class 2 – monthly earnings limits
(1) In this Schedule, subject to sub-paragraphs (2) and
(3) –
(a) the lower monthly
earnings limit for Class 2 contributions is £776;
(b) the standard monthly earnings
limit for Class 2 contributions is £3,686;
(c) the upper monthly
earnings limit for Class 2 contributions is £20,800.
(2) On
the 1st January in 2012 and every subsequent year, the limits in
sub-paragraph (1)(a) and (b) shall each be increased or decreased, as the
case requires, by the percentage figure equal to the percentage rise or fall in
the Jersey Index of Earnings during the 12 months ending on 30th June in
the preceding year.
(3) On
the 1st January in 2021 and every subsequent year, the limit in sub-paragraph (1)(c)
shall be increased or decreased, as the case requires, by the percentage figure
equal to the percentage rise or fall in the Jersey Index of Earnings during the
12 months ending on 30th June in the preceding year.
3 Class 2 – monthly full rate contributions
The amount of a person’s full
rate Class 2 contributions payable in any month is the aggregate of the
following amounts –
(a) 2%
of the standard monthly earnings limit, which amount shall be allocated to the
Health Insurance Fund;
(b) 10.5%
of the standard monthly earnings limit; and
(c) 2.5%
of the amount that is the difference between the standard monthly earnings
limit and the upper monthly earnings limit.
4 Class 2 – monthly reduced rate contributions
(1) The
amount of a person’s reduced rate Class 2 contributions payable in any
month is the aggregate of the following amounts –
(a) 2% of the person’s
earnings that do not exceed the standard monthly earnings limit, which amount
shall be allocated to the Health Insurance Fund;
(b) 10.5% of the person’s
earnings that do not exceed the standard monthly earnings limit; and
(c) 2.5% of the person’s
earnings that exceed the standard monthly earnings limit but do not exceed the
upper monthly earnings limit.
(2) The
references in sub-paragraph (1) to a person’s earnings shall be construed
in accordance with the provisions of an Order made under Articles 1(5)
and 8 by virtue of which the person is permitted to pay reduced rate
Class 2 contributions for the period in which the month for which the
contributions are payable falls.
4A Class 2 – standard contribution
(1) The
standard contribution for a month is, in the case of a Class 2 insured
person liable to pay full rate Class 2 contributions, the sum of –
(a) the maximum amount
payable under paragraph 3(b) for the month; and
(b) the maximum amount
payable under paragraph 3(c) for the month.
(2) The
standard contribution for a month is, in the case of a Class 2 insured
person liable to pay reduced rate Class 2 contributions whose earnings do
not exceed the standard monthly earnings limit, the maximum amount payable
under paragraph 4(1)(b) for the month.
(3) The
standard contribution for a month is, in the case of a Class 2 insured
person liable to pay reduced rate Class 2 contributions whose earnings
exceed the standard monthly earnings limit, the sum of –
(a) the maximum amount
payable under paragraph 4(1)(b) for the month; and
(b) the actual amount payable
by the person under paragraph 4(1)(c) for the month.
(4) The
references in sub-paragraphs (2) and (3) to a person’s earnings shall be
construed as described in paragraph 4(2).
5 Class 2 – supplementation
(1) No
supplementation shall be awarded for a month –
(a) in respect of full rate
Class 2 contributions; or
(b) in respect of reduced
rate Class 2 contributions, in a case where the Class 2 insured
person’s earnings are equal to or exceed the standard monthly earnings limit.
(2) Where –
(a) a Class 2 insured
person is liable to pay reduced rate contributions for a month;
(b) the person’s earnings are
less than the standard monthly earnings limit; and
(c) the sum of the social
security contributions paid and credited in respect of the person for the month
is –
(i) at least equal to the amount of the social
security contributions payable for the month in respect of the person by virtue
of paragraph 4(1)(b), but
(ii) less than the standard
contribution applicable in his or her case, described in paragraph 4A(2),
the social security
contributions shall be supplemented for the month by an amount sufficient to
cause them to equal that standard contribution.
(3) In
this paragraph –
(a) the references in
sub-paragraphs (1)(b) and (2)(b) to a person’s earnings shall be construed
as described in paragraph 4(2);
(b) “social security
contributions” means so much of the contributions paid or credited in respect
of a Class 2 insured person as are to be paid into the Social Security
Fund.
SCHEDULE 1C[169]
(Article 8AA(1))
Long-term care factors and
contribution rates
1 Insured person’s gross and taxable income
(1) For the purposes of calculating the amount of an LTC
contribution payable in respect of an insured person, and subject to any Order
made under Article 1(5) or 11 –
(a) an insured person’s gross
income for a year is the total of the sums calculated in accordance with
Article 4 of the 1961 Law for the year, before the deduction of any
amounts allowed under that Article;
(b) an insured person’s
taxable income for a year is so much of the person’s income for the year as is
charged to income tax.
(2) Where,
for the purposes of the 1961 Law, an insured person’s income of any
description includes that of his spouse or of his or her civil partner, it
shall also include that income for the purposes of calculating the amount of
the insured person’s LTC contribution.
2 Upper annual income limit
The upper annual income limit
for LTC contributions for a year is the annual equivalent of the upper monthly
earnings limit for Class 1 contributions for the year, determined in
accordance with paragraph 2(1)(c) and (3) of Schedule 1A.
3 LTC contribution
(1) An
insured person’s LTC contribution for a year is whichever is the lower of the
amount calculated in accordance with option A and the amount calculated in
accordance with option B.
(2) Option A
is that, subject to sub-paragraph (3), the person’s LTC contribution for a
year is the LTC percentage of the person’s taxable income for the year.
(3) If
the person is, for the year, entitled to a reduction in the amount of his or
her income tax under Article 92C of the 1961 Law, the person’s LTC
contribution shall be reduced by the same proportion by which the amount of
income tax payable by the insured person is reduced under that Article.
(4) Option B
is that, subject to sub-paragraph (5), the person’s LTC contribution for a
year is the LTC percentage of whichever is the lower of –
(a) the person’s gross income
for the year; and
(b) the upper annual income
limit for the year.
(5) Where
the insured person’s income includes, pursuant to the 1961 Law, the income
of his spouse or his or her civil partner, the rule in sub-paragraph (4)
shall be applied separately to –
(a) the income of the insured
person’s spouse or civil partner;
(b) the income of the insured
person, disregarding the income of his or her spouse or civil partner,
and the resultant amounts of
LTC contributions shall be aggregated.
(6) In
this paragraph, the LTC percentage is –
(a) for 2019, 1%;
(b) for 2020 and ensuing
years, 1.5%.
SCHEDULE 1D[170]
(Articles 8AA(3), 8AB(1)
and (3), 8AC(1) and 8AC(3))
collection of ltc
contributions
1 Interpretation of Schedule 1D
In this Schedule –
“building contractor” has the same meaning as in Article A15 of
the 1961 Law;
“Comptroller” has the meaning given by the Revenue Administration (Jersey) Law 2019;
“earnings” has the meaning given in Article A15 of the
1961 Law;
“employee” has the meaning given in Article A15 of the
1961 Law;
“employer” shall be construed having regard to the definition
“employee” and in accordance with Article A15(6) and (7) of the
1961 Law;
“sub-contractor” has the same meaning as in Article A15 of the
1961 Law;
“tax” means income tax;
“taxable income” has the same meaning as in paragraph 1 of
Schedule 1C.
2 Date by which LTC
contribution must be paid
(1) The Comptroller, when serving a notice of an assessment of tax
on an insured person under the 1961 Law may, at the same time, serve
notice of the amount of the LTC contribution that the person is liable to pay
for a year or an estimate of that amount.
(2) Subject
to paragraph 3 and to Articles 8AB(1) and 8AC(1), an LTC contribution
or an estimate of an LTC contribution notified under sub-paragraph (1) is
due and payable on the same day as the tax contained in the assessment.
(3) A
notice of the amount of the LTC contribution that a person is liable to pay or
an estimate of the person’s LTC contribution, served under sub-paragraph (1),
shall be deemed to be a demand for payment.
2A Estimate of LTC contribution
(1) An
estimate of the amount of a person’s LTC contribution for a year of assessment
shall be calculated in accordance with this paragraph.
(2) Schedule 1C
shall apply as if references in it to –
(a) the upper annual income
limit were references to that limit for the year of assessment; and
(b) subject to sub-paragraph (6), the person’s gross income and
taxable income, and the person’s entitlement to a reduction under Article 92C
of the 1961 Law,
were references to those
amounts or that entitlement –
(i) for the purposes
described in sub-paragraph (3) – for the year before the year of
assessment;
(ii)
(iii) for the purposes
described in sub-paragraph (5) – for the year of assessment.
(3) The
purposes referred to in sub-paragraph (2)(i) are –
(a) calculating an estimate
of the amount of a person’s LTC contribution for the purposes of
paragraph 1 of Schedule 1A to the 1961 Law;
(b)
(c) calculating the LTC
contribution effective rate of a taxpayer whose ITIS effective rate is
calculated under Article 41C of the 1961 Law.
(4)
(5) The
purposes referred to in sub-paragraph (2)(iii) are –
(a) serving a notice under
paragraph 2 of an estimate of the amount of the LTC contribution of a
taxpayer;
(b)
(6) Where
the calculation is to be made for the purpose of calculating a person’s LTC
contribution effective rate, in the case of a person whose ITIS effective rate
is calculated by reference to his or her estimated liability to income tax for
a year, the amounts referred to in sub-paragraph (2)(b) shall also be
estimates.
3 Duty of insured person to pay instalment of LTC contribution
An insured person who is
liable to pay an instalment of tax for a year of assessment, in accordance with
Article 41A of the 1961 Law, is also liable to pay an instalment of
his or her LTC contribution for the year in which the instalment is due, at the
same time and in the same manner as the instalment of tax, in accordance with Article 49B
and paragraph 1 of Schedule 1A to the 1961 Law.
4 LTC contribution effective rate
(1)
(2) The
LTC contribution effective rate applicable in an employee’s case shall be
determined in accordance with the following formula –
L
x 100 = LTC contribution effective rate
I
Where –
L is the sum of –
(a) the employee’s estimated
LTC contribution for the year to which the rate applies, calculated in
accordance with paragraph 2A; and
(b) an amount not exceeding
the aggregate of any LTC contributions unpaid for any preceding years; and
I is the estimated sum, for the year to which the rate applies,
of the amount of income for which the employee is liable to be assessed and the
amount of income from which the employee is liable to allow the deduction of
tax.
(3)
(4)
(5) Where
an employee makes a request under Article 41CB of the 1961 Law which has
been approved by the Comptroller, the Comptroller shall calculate an LTC
contribution effective rate that exceeds the rate that would otherwise apply in
the employee’s case, in accordance with the foregoing provisions of this
paragraph, by an amount that corresponds to the amount by which the new rate of
tax exceeds the rate that would otherwise apply in the employee’s case.
(6) If,
on an appeal by an employee against the effective rate of tax applicable in his
or her case, that rate is revised, the Comptroller –
(a) shall correspondingly
revise the LTC contribution effective rate applicable in the employee’s case;
and
(b) shall calculate a revised
combined effective rate applicable in the employee’s case.
4A Surcharge for late payment of LTC contribution
(1) In
this paragraph, “specified time” has the meaning given by Article 41I(1)
of the 1961 Law.
(2) An
insured person who is liable to pay an LTC contribution for a year shall be
liable to pay an amount in addition to that contribution (hereafter referred to
as the “LTC surcharge”) equal to 0% of so much of the LTC contribution for the
year which remains unpaid, if the LTC contribution for the year is not paid in
full by the specified time.
(3) A
person shall not be liable to pay the LTC surcharge if –
(a) the Comptroller has,
under Article 41I(2) of the 1961 Law, waived the person’s payment of
the tax surcharge due; or
(b) the person is not, by
virtue of Article 41I(3) of the 1961 Law, liable to pay the tax
surcharge.
(4) If,
on an appeal under Article 41I(7) of the 1961 Law, the Commissioners
direct that a person’s liability under Article 41I(2) shall be waived, the
person’s liability to the LTC surcharge shall be taken to have been waived.
(5) In
this paragraph “tax surcharge” means a surcharge that a person is liable to pay
under Article 41I of the 1961 Law.
5 Consequences of appeal against assessment to tax
(1) Where
an insured person appeals against any assessment on him or her made by the
Comptroller in any first or additional assessment –
(a) the insured person, when
estimating his or tax in accordance with Article 28(2) of the
1961 Law, shall also estimate his or her LTC contribution that will become
payable consequentially on the determination of the appeal;
(b) pending the person’s
appeal against his or her assessment to income tax, the LTC contribution
estimated in accordance with clause (a) shall be due and payable at the
same time as his or her tax estimated in accordance with Article 28(2) of
the 1961 Law and due and payable as described in paragraph (3) of
that Article; and
(c) where, on determination
of the appeal, a balance of tax chargeable must be paid in respect of a portion
of the insured person’s income, the balance of any corresponding LTC
contribution payable in respect of that portion of the insured person’s income
is also due, and must be paid at the same time and in the same manner as the
balance of tax.
(2) Where –
(a) an insured person appeals
against a notice of assessment served under Article 25 of the
1961 Law or against a determination by the Commissioners under Article 36
of the Law; and
(b) on determination of the
appeal, a balance of tax overpaid is required to be repaid,
the corresponding balance of
any LTC contribution that has been overpaid must be repaid at the same time and
in the same manner.
(3) Where,
on an appeal under Article 36 of the 1961 Law, any balance of tax is
to be paid or repaid, the corresponding balance of any LTC contribution that
has been underpaid or overpaid must be paid or, as the case requires, repaid,
at the same time and in the same manner.
6 Consequences of error in or adjustment of assessment to tax
(1) Where,
in the circumstances described in Article 37 or 38 of the 1961 Law, a
repayment of tax is due to an insured person, any corresponding overpayment of
the insured person’s LTC contribution shall also be due and repaid at the same
time, and in the same manner, as the repayment of tax.
(2) Where
an insured person is repaid an amount formerly paid for tax for a year of
assessment under Part 13 of the 1961 Law, the person shall also be
repaid any corresponding amount of LTC contribution that was aggregated with
and paid by the person together with the amount formerly paid for tax.
7 Age determination
If a person, by reason of
attaining an age during the course of a month, becomes liable for contributions
or different amounts of contribution, the Social Security Department shall
determine whether any such contribution is payable in respect of that month
either by treating the person as having attained that age at the beginning of
the month or as not having attained that age until the end of the month.
SCHEDULE 1
(Articles 13 and
27)
PART 1 – Rates of Benefit[171]
|
Description of Benefit.
|
Weekly Rate.
|
|
1.
|
Short term incapacity allowance .....................
|
Standard rate of benefit.
|
|
2.
|
Incapacity
pension .......
|
Standard rate of benefit.
|
|
2A.
|
Home
carer’s allowance …………….
|
Standard rate of benefit.
|
|
4.
|
Parental allowance .......
|
Standard rate of benefit.
|
|
5.
|
Survivor’s allowance ...
|
120% of the standard rate of benefit.
|
|
6.
|
Survivor’s
pension .......
|
Standard rate of benefit.
|
part 1A – rates of old age pension[172]
1 Interpretation of Part 1A
(1) For the purposes of this Part of this
Schedule –
“standard rate” shall be construed in accordance with
paragraph 2;
“RPI (Pensioners)” means the Jersey Retail Prices Index (Pensioners)
produced by the States of Jersey Statistics Unit.
(2) For the purposes of this Part of this
Schedule –
(a) a reference to the RPI (Pensioners)
for a year or to the Jersey Index of Earnings for a year is a reference to that
index after the percentage increase or decrease in the index for the year has
been applied; and
(b) the percentage increase
or decrease in the RPI (Pensioners) or the Jersey Index of Earnings for a year
is the percentage increase or decrease in that index during the 12 months
commencing July of the preceding year.
2 Standard rate
(1) The standard rate for the period beginning
7 days after the date prescribed for the purposes of Article 25A(1)(a)
and ending with 30th September 2013 shall be £189.84.
(2) The standard rate shall be recalculated on
1st October 2013 and on each anniversary of that date, in accordance
with the following provisions of this paragraph.
(3) If, for a year, the RPI (Pensioners)
increases and the Jersey Index of Earnings either does not increase or
increases by a percentage that is less than the percentage increase in the RPI
(Pensioners), the standard rate shall be increased by the same percentage as
the percentage increase in the RPI (Pensioners) for the year.
(4) Subject to sub-paragraph (5) if, for a
year –
(a) the RPI (Pensioners)
increases but the increase is by a percentage that is less than the percentage
increase in the Jersey Index of Earnings;
(b) the RPI (Pensioners)
stays the same but the Jersey Index of Earnings increases; or
(c) the RPI (Pensioners)
decreases and the Jersey Index of Earnings for the year increases or remains
the same,
the standard rate shall be adjusted by the percentage change that is
the arithmetic mean of the percentage change in the RPI (Pensioners) for
the year and the percentage change in the Jersey Index of Earnings for the
year.
(5) If, for a year, the application of the rule
in sub-paragraph (4) would result in the Pension Index for the year being
less than the Jersey Index of Earnings for the year, the standard rate shall
instead be increased by the percentage required to increase the Pension Index
for the year so as to equal the Jersey Index of Earnings for the year.
(6) For the purposes of sub-paragraph (5) –
(a) the Pension Index for
2012 is 275.1;
(b) the Pension Index for
each subsequent year is the amount that is the Pension Index for the preceding
year increased by the same percentage as the percentage increase (if any) in
the standard rate on 1st October in that subsequent year.
(7) If, for a year, there is no increase in
either the RPI (Pensioners) or the Jersey Index of Earnings, the standard rate
shall remain unchanged.
3 Rates of old age
pension
(1) The weekly rate for the old age pension is
the standard rate.
(2) The weekly rate for a reduced old age
pension taken in accordance with Article 25(1A) is the rate of old age
pension payable to the person, reduced by 0.58% for each month from the month in
which the person becomes entitled to receive the reduced old age pension until
the month in which the person attains pensionable age (both months inclusive).
(3) The weekly rate payable for an old age
pension where the pension is payable to a woman by virtue of her husband’s
insurance, and the woman’s husband is alive, is 66% of the rate of old age
pension payable to her husband.
PART 2 – Amounts of SINGLE PAYMENT BENEFITS[173]
|
Description
of Grant.
|
Amount.
|
|
1.
|
Parental
grant...............
|
A lump sum equal to 3 times the
standard rate of benefit.
|
|
2.
|
Death
grant ..................
|
A lump sum equal to 4 times the
standard rate of benefit.
|
|
3.
|
2013
old age pension adjustment
|
A lump sum that is the relevant
percentage of the prescribed amount – where the relevant percentage is
the percentage of the old age pension that, on the date prescribed for the
purposes of Article 25A(1)(a), the person is, in accordance with this
Law and any Order made under it, eligible to receive.
|
PART 3 – Increase for dependant[174]
|
Increase
for dependant
|
66% of
the rate of benefit payable to the beneficiary.
|
SCHEDULE 2[175]
(Article 14)
CONTRIBUTION CONDITIONS
1 Short term incapacity allowance
(1) The
contribution conditions for short term incapacity allowance are that –
(a) the claimant has paid
contributions prior to the end of the relevant quarter and the annual
contribution factor derived from those contributions is not less than 0.25; and
(b) the claimant has either
paid or been credited with contributions in respect of the relevant quarter and
the quarterly contribution factor derived from those contributions is 1.00.
(2) In
this paragraph the expression “relevant quarter” means the previous quarter but
one before the quarter in which the entitlement to short term incapacity
allowance first arises.
2 Long term incapacity allowance
(1) The
contribution conditions for long term incapacity allowance are that –
(a) the claimant has paid
contributions prior to the end of the relevant quarter and the annual
contribution factor derived from those contributions is not less than 0.5; and
(b) the claimant has either
paid or been credited with contributions in respect of the relevant quarter and
the quarterly contribution factor derived from those contributions is 1.00.
(2) In
this paragraph the expression “relevant quarter” means the previous quarter but
one before the quarter in which entitlement to long term incapacity allowance
first arises.
3 Incapacity pension
(1) The
contribution conditions for incapacity pension are that –
(a) the claimant has paid
contributions prior to the end of the relevant quarter and the annual
contribution factor derived from those contributions is not less than 0.5; and
(b) the claimant has either
paid or been credited with contributions in respect of the relevant quarter and
the quarterly contribution factor derived from those contributions is 1.00.
(2) In
this paragraph the expression “relevant quarter” means the previous quarter but
one before the quarter in which entitlement to incapacity pension first arises.
3A Home carer’s allowance
(1) The
contribution conditions for home carer’s allowance are that –
(a) the claimant has paid
contributions prior to the end of the relevant quarter and the annual
contribution factor derived from those contributions is not less than 0.5; and
(b) the claimant has either
paid or been credited with contributions in respect of the relevant quarter and
the quarterly contribution factor derived from those contributions is 1.00.
(2) A
married woman who has made an election under Article 3 of the Social Security (Married
Women) (Jersey) Order 1974 and whose election has not been cancelled
shall be taken to satisfy the contribution conditions in sub-paragraph (1).
(3) In
this paragraph the expression “relevant quarter’” means the previous quarter
but one before the quarter in which entitlement to home carer’s allowance first
arises.
4 Parental allowance
(1) The
contribution conditions for parental allowance are that –
(a) the claimant has paid contributions
prior to the end of the relevant quarter and the annual contribution factor
derived from those contributions is not less than 0.25; and
(b) the claimant has paid or
been credited with contributions in respect of the relevant quarter and the quarterly
contribution factor derived from those contributions is 1.00.
(2) In
this paragraph the expression “relevant quarter” means the previous quarter but
3 before the quarter in which the beginning of the parental allowance period
falls.
5 Parental grant
(1) The
contribution conditions for parental grant are that the relevant person has
paid contributions prior to the end of the relevant quarter and the annual
contribution factor derived from those contributions is not less than 0.25.
(2) In
this paragraph –
(a) the expression “relevant person” means the person by whom the conditions are to be satisfied;
(b) the
expression “relevant quarter” means the previous
quarter but one before the quarter in which it is expected that the relevant
person’s child will be born or adopted.
6 Survivor’s benefit and old age pension
(1) The
contribution conditions for survivor’s benefit or old age pension are
that –
(a) the relevant person has
paid contributions before the relevant time and the annual contribution factor
derived from those contributions is not less than 0.5; and
(b) the life average
contribution factor derived from the contributions paid by or credited to that person
(as at the relevant time) is 1.00.
(2) In
this paragraph –
(a) the expression “relevant person”
means –
(i) in the case of a survivor’s benefit, the
deceased spouse or deceased civil partner, and
(ii) in the case of an old
age pension, the person claiming the pension;
(b) the expression “relevant
time” (except in the case to which clause (c) refers) means the date of
the relevant person attaining pensionable age or dying under that age;
(c) the expression “relevant
time”, in the case of a reduced old age pension under Article 25(1A),
means the date at which the relevant person becomes entitled to the reduced
pension.
7 Death grant
(1) The
contribution conditions for a death grant are that –
(a) a contribution was
payable by the relevant person in respect of the contribution month in which
the death occurred; or
(b) the relevant person has
paid contributions prior to the end of the relevant quarter and the annual
contribution factor derived from those contributions is not less than 1.00.
(2) In
this paragraph –
(a) the expression “relevant person” means the person by whom the conditions are to be satisfied;
(b) the expression “relevant quarter” means the previous quarter but one before the quarter in which the
death occurred or, where immediately before the date of the deceased’s death
the relevant person was dead or over pensionable age, the previous quarter but
one before the quarter in which that person attained pensionable age or died
under that age.
SCHEDULE 3[176]
(Article 49)
OATHS OF OFFICE
Form of oath to be taken by
the Controller.
You swear and promise
before God that you will well and faithfully discharge the duties of Controller
of Social Security in accordance with the laws relating to social security;
that you will conduct yourself without hatred, favour or partiality; that you will
exercise the powers entrusted to you by the said laws in such manner only as
shall appear to you to be necessary for the due execution of the same; and that
you will not disclose any information which may come to your knowledge in the
performance of your duties except to such persons only as shall act in
execution of the said laws and where it shall be necessary to disclose the same
to them for the purposes of the said laws, or in so far as you may be required
to disclose the same for the purposes or in the course of a prosecution for an
offence against the said laws, or in such cases as you are expressly authorized
by the said laws to disclose the same.
SCHEDULE 4[177]